Figure 8. XID mice have significantly more IFN-γ+ NK/NKT cells after SchuS4 infection compared to WT mice.
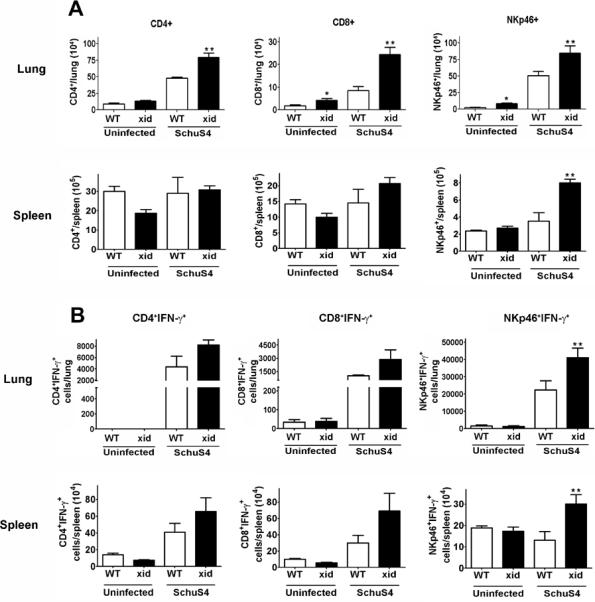
Mice (n=4–5/group) were intranasally infected with 50 CFU F. tularensis strain SchuS4. As indicated, animals received 5 mg/kg levofloxacin on days 3–6 of infection. Animals were euthanized on day 7 of infection and single cell suspensions of the lung and spleen were generated. Cells were incubated with PMA, ionomycin, and BFA for 4 hours, were stained for specific surface receptors, permeabilized and stained for IFN-γ and assessed for specific cell populations by flow cytometry. Error bars represent SEM. * = significantly greater than uninfected WT (p<0.05). ** = significantly greater than all other groups (p<0.05). Data is representative of two experiments of similar design.
