Figure 3.
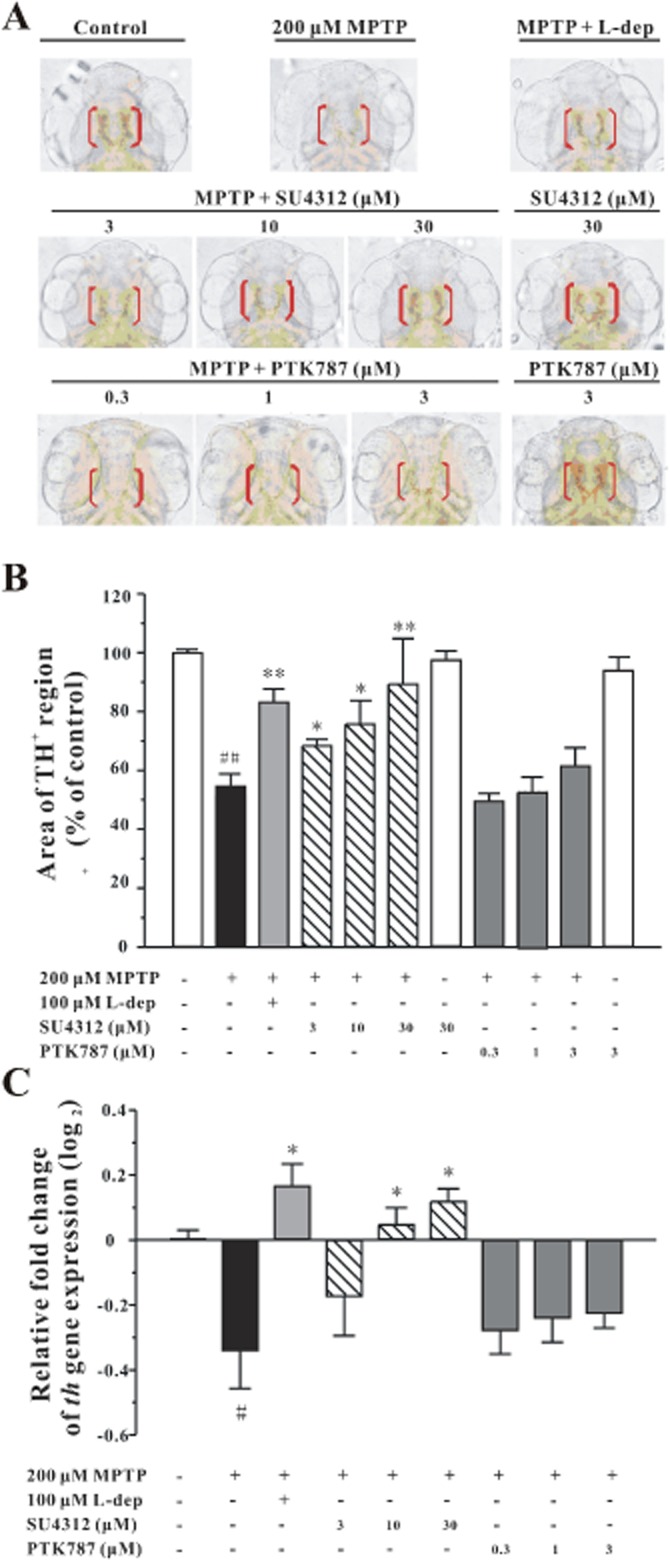
SU4312 protects against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Zebrafish embryos (1 dpf) were co-incubated with 200 μM MPTP and SU4312 or PTK787/ZK222584 at the indicated concentrations for 48 h, and zebrafish embryos that had been co-treated with MPTP and 100 μM L-deprenyl (L-dep, aMAO-B inhibitor) were used as the positive control. After treatment, zebrafish were collected to carry out immunohistochemistry, or total RNA extraction and real-time quantitative PCR. (A, B) SU4312, but not PTK787/ZK222584, prevents MPTP-induced TH+ neuronal loss in the brain of zebrafish in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) Representative pictures of dopaminergic neurons in the zebrafish brain from different treatment groups. Immunohistochemistry was performed with anti-TH primary antibody, and TH+ neurons in the diencephalic area of the zebrafish brain were considered as DA neurons. (B) Analysis of TH+ neurons in each treatment group, 20 fish embryos per group from three time-independent experiments. Values are expressed as a percentage of the control. (C) SU4312, but not PTK787/ZK222584, reverses th gene expression down-regulated by MPTP. Data were expressed as relative fold change of control (log2), *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus MPTP group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus control (Tukey's test).
