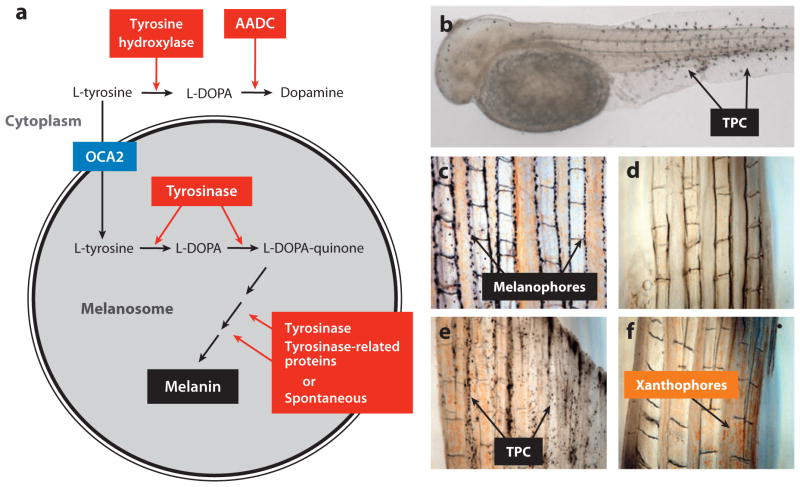
Figure 10.
Cavefish tyrosinase-positive albinism. (a) A summary of steps in which L-tyrosine is converted to melanin in the melanosome and dopamine in the cytoplasm showing the key roles of tyrosinase, other enzymes, and the presumed role of OCA2 as an L-tyrosine transporter. (b) Melanophores revealed in an albino Pachón cavefish embryo after conversion of exogenous L-DOPA to melanin by active tyrosinase. TPC: tyrosinase positive cells (melanophores). (c,d) Explants of surface fish (c) albino Pachón adult tail fin (d) showing melanophores in the former but not the latter. (e) Albino Pachón adult tail fin explant in which tyrosinase positive cells are revealed by L-DOPA treatment and melanin deposition. (f) Albino Pachón adult tail fin explant showing inability to convert exogenous L-tyrosine to melanin. The presence of xanthophores is also indicated in albino Pachón adult tail fin explants. (a–f) from McCauley et al. (2004).