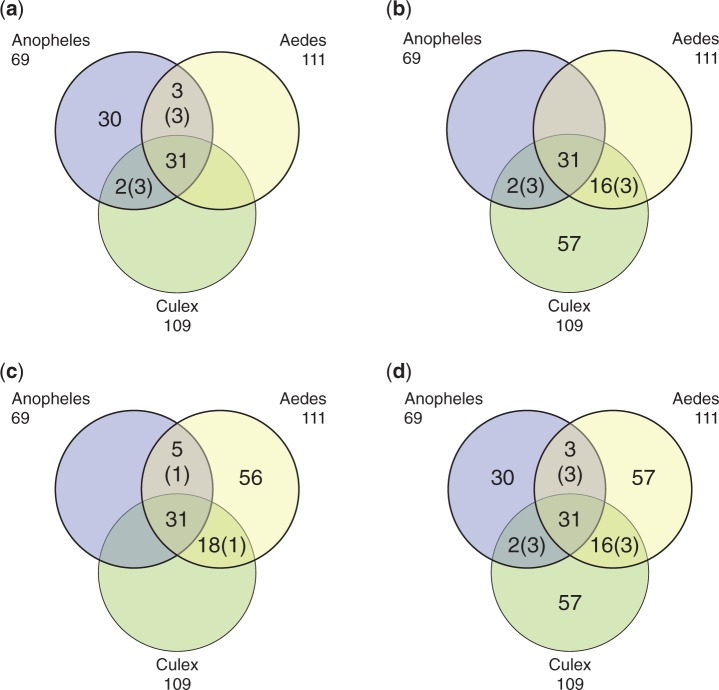
Fig. 3.—
Analysis of orthologous OBP genes shared across three mosquito species, Anopheles gambiae, Aedes aegypti, and Culex quinquefasciatus. The Venn diagrams indicate the number of inferred orthologous genes shared among the mosquitoe species: (a) number of A. gambiae OBP genes orthologous to Aed. aegypti and C. quinquefasciatus; (b) number of Aed. aegypti OBP genes orthologous to A. gambiae and C. quinquefasciatus; (c) number of Culex OBP genes orthologous to A. gambiae and Aed. aegypti; (d) overall number of orthologous groups across the three mosquito species. The orthologs were identified using the reciprocal BLAST hit approach. The number of genes that share a three-way (1:1:1) orthology between the three species is 31. The number of genes in a species that have two-way orthology (1:1) with the two other species but not a three-way orthology is indicated between parenthesis and for a given species should be counted only once. For example, in (a), the total number of OBP genes in A. gambiae is 30 + 3 + 2 + 31 + (3) = 69, since three genes in A. gambiae have two-way orthology (1:1) with genes in both C. quinquefasciatus and Aed. aegypti but not a three-way orthology. Detailed listings of the orthology analysis are provided in supplementary table S1a, c, and e, Supplementary Material online.