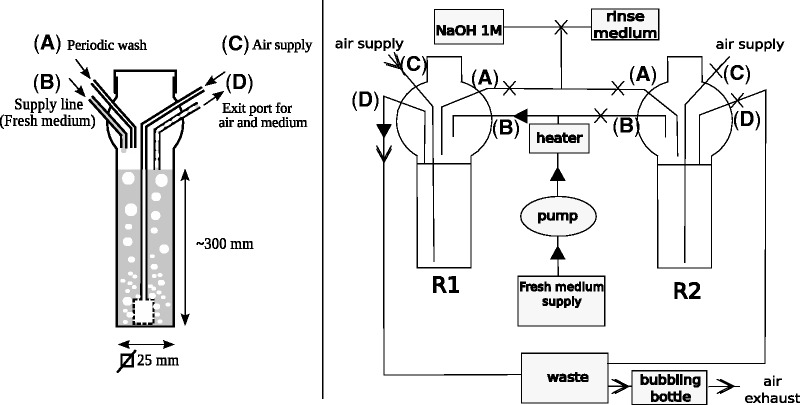
Fig. 1.—
Left: Diagram of a single reactor during the culture stage. The reactor has been assembled by glass blowing, and incorporates a square cross-section glass tube in the bottom portion, and a screwed plastic cap on top. The entry and exit tubes are welded to the top of the reactor and comprise an air supply connected to a tube that is terminated by a porous glass plug at the bottom of the reactor (generating bubbles that give both aeration and mixing via air lift) (C), a fresh supply of medium (B), a wash fluid entry point (A), a fluid exit, and a biphasic mixture of air and liquid (D). Right: Schematics of the tubing connections during the culture phase in the reactor R1. R1 and R2 are the two reactors of the setup; each is temperature regulated; filtered air (rate adjusted by a flow meter/needle valve) is injected through port (C) of reactor R1. It passes through a porous glass plug and generates bubbles serving for both culture aeration and mixing via air lift within the reactor. The bottle containing the fresh medium is connected to a peristaltic pump; a constant flow of medium arrives at port (B) of reactor R1. A heating resistance heats the medium before entry (B), to prevent backward contamination of the supply of medium; the reactor wash solution (connected to port (A) and not used at this stage of operation of R1) comprises NaOH 1 M and rinse medium (the same solution as the supply of medium to the reactor); a waste bottle is connected to port (D) of reactor R1. It receives a biphasic mixture of air and medium exiting from the reactor by a common path and traps the liquid; the air exiting from the waste bottle is bubbled through bleach in a bubbling bottle, so as to avoid laboratory air contamination. The full arrows indicate the circulation of liquids, and the open arrows indicate the circulation of air. Crosses indicate the pinched-closed sections of tubes. Every week, the content of the operating reactor is transferred to the already cleaned tandem reactor. During the transfer phase (e.g., from R1 to R2), port (D) of R1 is closed and ports (A), (B), and (C) are open; ports (B) and (C) of R2 are closed and ports (A) and (D) are open. Air and medium containing bacteria come from R1 to R2 through port (A). When the transfer is stopped, R2 enters the culture phase, and R1 is rinsed and washed and ready for the next transfer.