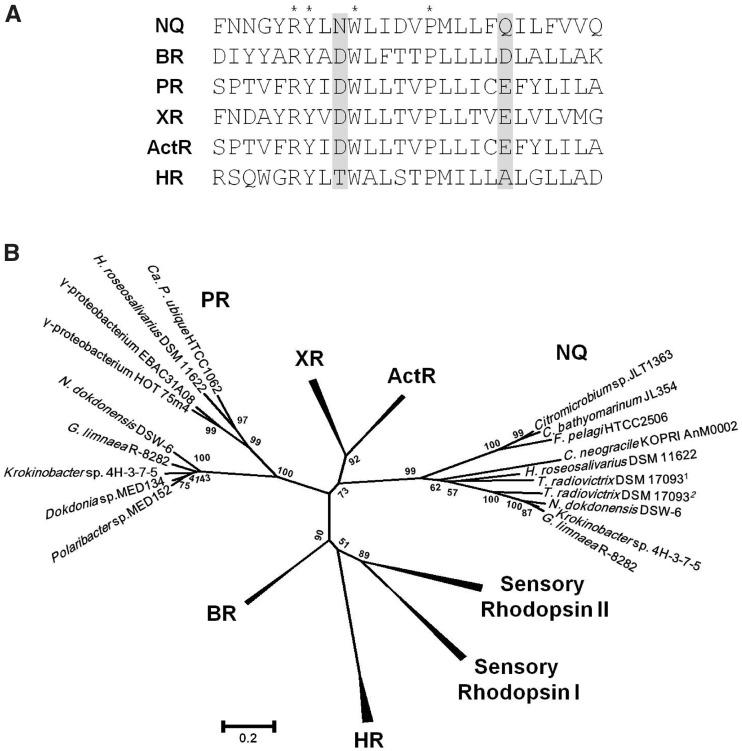
Fig. 2.—
Characteristic features of the new family of rhodopsins that contain the NQ motif. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the third transmembrane helix of the NQ rhodopsin of Nonlabens (Donghaeana) dokdonensis DSW-6 and representative microbial rhodopsins. Asterisks, invariant residues; shaded, active site residues of microbial rhodopsins. (B) Phylogenetic relationships among microbial rhodopsins. A tree inferred from 199 conserved amino acid positions was constructed using MEGA5. Bootstrap values for 1,000 replicates are shown next to the branches. NQ, NQ rhodopsin; BR, bacteriorhodopsin; PR, proteorhodopsin; XR, xanthorhodopsin; ActR, actinorhodopsin; HR, halorhodopsin. Accession numbers: Citromicrobium sp. JLT1363, ZP_08702831; Citromicrobium bathyomarinum JL354, ZP_06860850; Fulvimarina pelagi HTCC2506, ZP_01440547; Chaetoceros neogracile KOPRI AnM0002, EL620625; Truepera radiovictrix DSM 170931, YP_003705905; T. radiovictrix DSM 170932, YP_003706581; Gillisia limnaea R-8282, ZP_09669334; Krokinobacter (Dokdonia) sp. 4H-3-7-5, YP_004429763; Hymenobacter roseosalivarius DSM 11622, gene ID 2502504185 or locus tag HrosDRAFT_3745 in the IMG database.