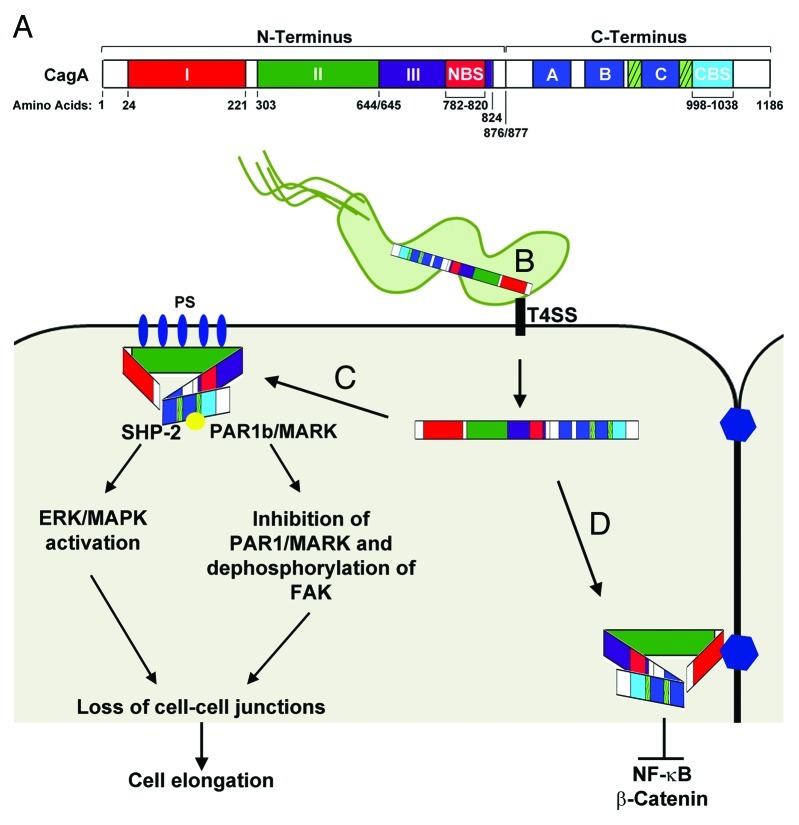
Figure 1. CagA Functional Domains. (A) Linear representation of CagA domains. The CagA N-terminus (1–876) contains three domains (I, II, and III). Domain I spans residues 24–221, Domain II spans residues 303–644, and Domain III spans residues 654–824. A N-terminal binding sequence (NBS) is located within Domain III from residues 782–820. The CagA C-terminus (877–1186) contains the EPIYA-ABC motifs (dark blue boxes), the Cag multimerization sequences (hatched boxes), and a C-terminal binding sequence (CBS) located from residues 998–1038.90 (B) The first 200 amino acids of the N-terminus (Domain I) target CagA inside H. pylori to the type IV secretion system (T4SS). The T4SS interacts with β-1 integrin (black rectangle) and is responsible for translocation of CagA into the epithelial cell. Residues 800–1216 alone target CagA to the cytoplasm.88 (C) CagA interacts with phosphatidylserine (PS; blue ovals) on the inner surface of the plasma membrane via basic residues located on Domain II. Interaction of the NBS and CBS condenses the structure of CagA allowing the unstructured C-terminus to remain accessible to Src-kinases as well as SHP-2. Phosphorylation of CagA (yellow circle) by Src-kinases results in activation of SHP-2 and the ERK/MAPK pathways leading to cell elongation. (D) Targeting of CagA to cell-cell junctions by Domain I results in inhibition of NF-κB and β-catenin and inhibition of EPIYA mediated cell signaling pathways. For more detailed information concerning the signaling pathways affected by CagA see78. Figure was adapted from.89,90,92

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.