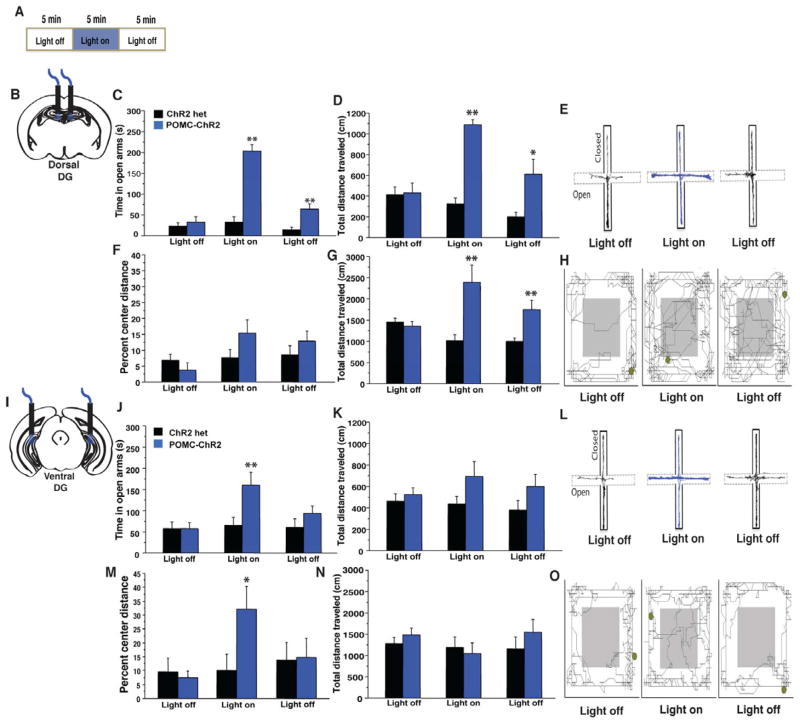
Figure 6. GCs in the ventral DG control conflict anxiety, while those in the dorsal DG drive exploratory behavior.
A) Experimental design. POMC-ChR2 mice and single transgenic littermate controls were implanted in the dorsal (B–G) or ventral (I–O) DG then tested for 15min in the EPM and OFT with 5min light off, 5min light on, 5min light off epochs. (C–D) Optical stimulation of the dorsal DG in POMC-ChR2 mice but not single transgenic controls increased total time in the open arms of the EPM (C, repeated measures ANOVA, genotype effect F(1,15)=54.1, p<0.0001, light effect, F(2,30)= 42.2, p<0.0001, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=30.2, p<0.0001, t test light on t15= −8.4, p<0.0001) as well as total distance traveled in the maze (genotype effect F(1,15)=18, p<0.001, light effect, F(2,30)= 16.3, p<0.0001, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=20.3, p<0.0001, t test light on t15= −9.9, p<0.0001) Track trace represented in (E) (F–G) Optical stimulation of the dorsal DG in POMC-ChR2 mice but not single transgenic controls increased total exploration in the OFT but not percent distance traveled in the center of the arena (n=8–9/geno, total distance traveled, repeated measures ANOVA, genotype effect F(1,15)=8.3, p=0.01, light effect, F(2,30)= 3.2, p=0.05, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=14.3, p<0.0001, t test light on t15= 3.3, p=0.004, percent center distance F(1,15)=1.1, p=0.31, light effect, F(2,30)= 3.5, p=0.04, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=2.4, p=0.1, t test light on t15= 1.5, p=0.14). Track trace in (H). J–K) Ventral DG stimulation was acutely anxiolytic in the EPM as light stimulation increased time POMC-ChR2 mice spent in open arms of the maze (n=8/geno, repeated measures ANOVA, genotype effect F(1,14)=3.2, p=0.1, light effect, F(2,28)= 4.6, p=0.02, light X genotype interaction F(2,28)=4, p=0.03, t-test on light epoch t14=−2.4, p=0.03), but did not impact total distance traveled in the maze, genotype effect F(1,14)=3.4, p=0.1, light effect, F(2,28)= 0.7, p=0.5, light X genotype interaction F(2,28)=1, p=0.4). Track trace in L). M–N) OFT. Ventral DG stimulation did not impact total locomotor activity, but increased the percent distance traveled in the center of the arena (n=8–9/geno, repeated measures ANOVA, total distance traveled, genotype effect F(1,15)=0.3, p=0.6, light effect, F(2,30)= 1.9, p=0.2, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=1.6, p=0.2, percent center distance, genotype effect F(1,15)=0.9, p=0.2, light effect, F(2,30)= 6.4, p=0.005, light X genotype interaction F(2,30)=6.9, p=0.003, t test light on t15=2.2, p=0.04, track trace in O). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. All error bars are +/− SEM.