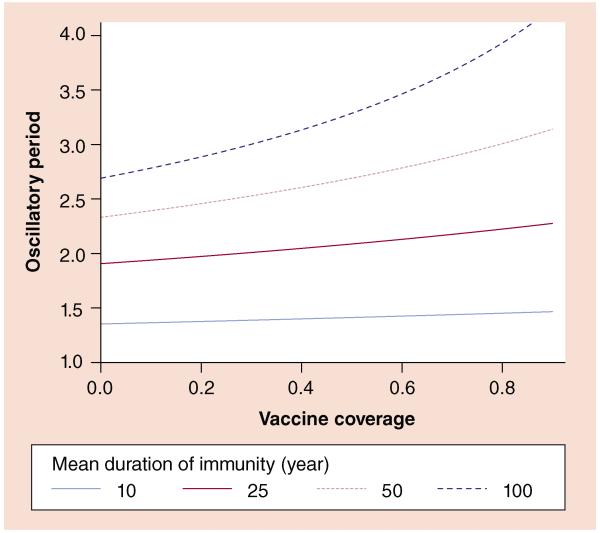
Figure 2. Impact of vaccine coverage and loss of immunity on a predicted interepidemic period.
The dark, dashed line shows that when immunity is long lasting, the interepidemic period is sensitive to vaccine coverage, ranging from 2.7 years in the absence of vaccination to 4.2 years with 90% coverage. For scenarios in which immunity is lost more rapidly, the interepidemic period is shorter and less sensitive to vaccination. All curves were calculated according to [22] with the following parameter values: per capita annual birthrate (μ) of 0.02; mean infectious period (1/γ) of 21 days; transmission rate (β) of 200 per year, corresponding to a basic reproductive number (R0) of 11.5.