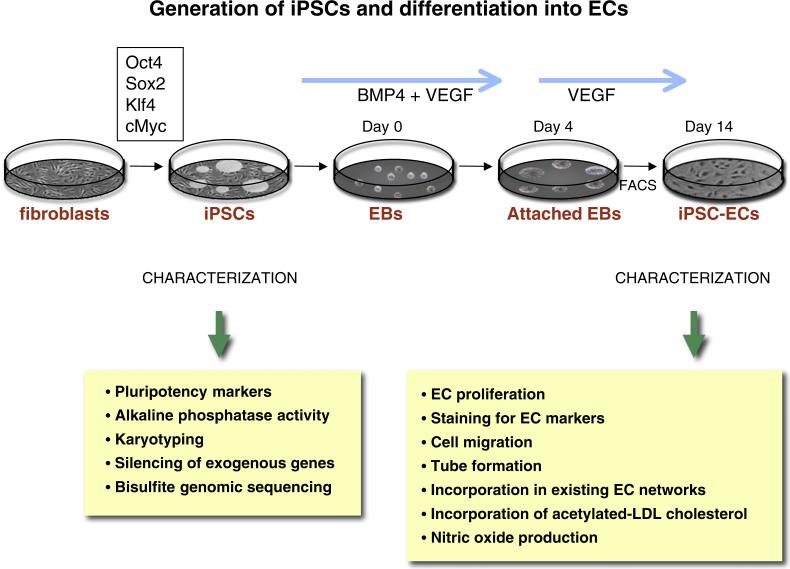
Fig. 1.
Generation of iPSCs and differentiation into ECs. IPSCs may be generated by overexpressing Oct4, Sox2, Klf 4 and cMyc (using retroviral, mmRNA, or cell-permeant peptide constructs). The iPSCs are characterized by staining for pluripotency markers and alkaline phosphatase activity. Other tests for quality of the reprogramming include spectral karyotyping, and bisulfite genomic sequencing to assess genomic and epigenomic quality. Endothelial differentiation is initiated by culturing hiPSCs for 14 days in differentiation media supplemented with 50 ng/ml bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) and 50 ng/ml vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The heterogenous mixture of cells is purified by FACS using an antibody directed against CD31. The ECs can be characterized for functionality by looking at the ability of iPSC-ECs to proliferate (using BrdU), the ability to generate capillary-like structures (when grown in matrigel) and the ability to incorporate in a pre-existing EC network. Other functional tests include the ability of the IPSCs-ECs to incorporate acetylated-LDL cholesterol, to produce nitric oxide, and to express markers such as KDR, CD31, CD144, and eNOS.