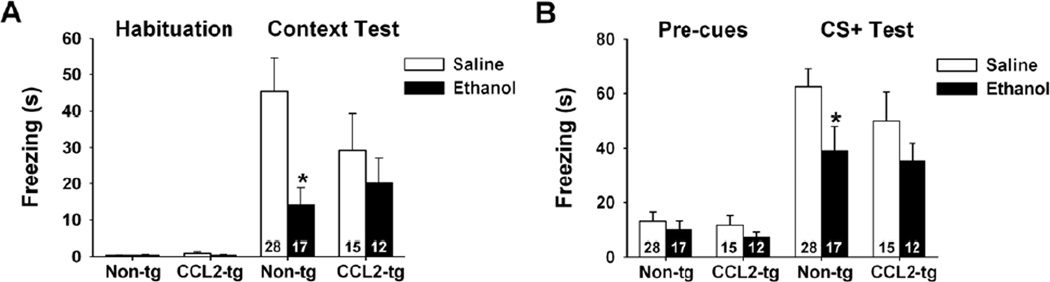
Fig. 6.
Effect of acute ethanol on cued and contextual fear conditioning. For fear conditioning, mice were treated with ethanol (1 g/kg) or saline prior to the conditioning trial. (A) Freezing responses during habituation and during exposure to contextual cues. (B) Freezing responses before the cue was activated (pre-cue) and during cue exposure in the conditioned stimulus (CS+ test). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of the time (s) spent freezing. Non-tg mice treated with ethanol showed significantly less freezing behavior during both the context test (p=0.007) and CS+ test (p=0.037) compared to control non-tg mice treated with saline. The number of animals studied for each test is marked in the corresponding bar. * Indicates a significant difference between ethanol and saline treated mice of the same genotype.