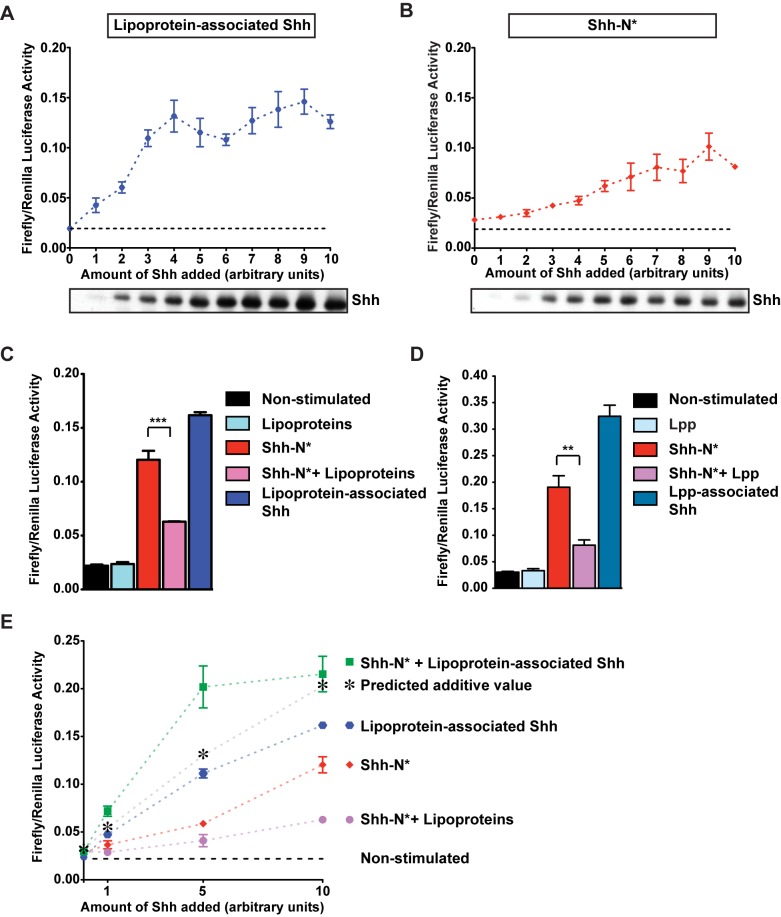
Figure 7. Signaling properties of lipoprotein-associated Shh and Shh-N* in Shh-LIGHT2 cells.
(A, B) Concentration-dependent signaling activity of (A) lipoprotein-associated Shh and (B) Shh-N*. Lipoprotein concentration in (A) was kept constant, and only the fraction carrying Shh increased. Shh and Shh-N* levels used for signaling assays were assessed by WB. (C,D) Shh pathway activity in cells stimulated by Shh-N* in the absence or presence of lipoproteins, or cells stimulated with lipoprotein-associated Shh. Lipoproteins, where added, were kept at a constant level. (C) Mammalian lipoproteins, (D) Drosophila Lpp. (E) Synergistic signaling activity of Shh-N* and lipoprotein-associated Shh. Shh-N* and lipoprotein-associated Shh were applied to cells alone or in combination. Predicted additive values represent the combined activity of lipoprotein-associated Shh and Shh-N* in the presence of lipoproteins, minus the basal assay activity measured in unstimulated cells. Note that the same batch of samples was used for assays shown in (A) and (B). For (A–E), error bars indicate ± SD (n = 3; **p<0.005; ***p<0.0005) of one representative experiment. Experiments were repeated at least twice.