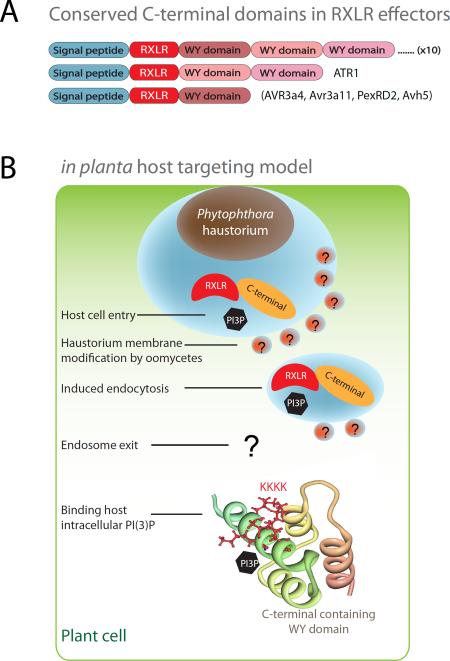
Figure 4. Conserved RxLR-dEER effector structure fold and different sites for PI(3)P binding.
(a) RxLR effector domain architecture. RxLR effectors have an N-terminal secretory leader, a host targeting RxLR motif and conserved C-terminal domains that are often arranged into tandem repeats. (b) Host targeting model and involvement of PI(3)P at different cellular sites. The N-terminal RxLR motifs play an important role in host cell entry at host plasma membrane; and in vitro recombinant proteins of Avr1b bind PI(3)P. The C-terminal region has a conserved effector fold and is able to suppress host defense responses. The positive patches in the C-terminal domain of Avr1b and Avr3a are important for PI(3)P and PI(4)P binding. The Avr1b C-terminal structure is used in the illustration. Several important conceptual steps such as modification of membrane by pathogen are postulated and indicated with question marks.