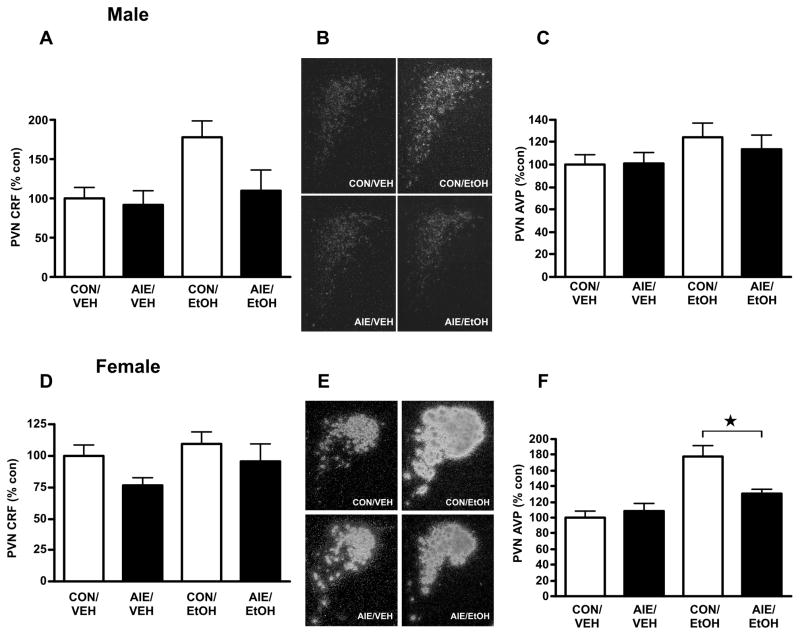
Figure 3.
Effects of intermittent alcohol vapor exposure during adolescence on Crf and Avp mRNA expression in the PVN of adult (PND 70–71) male (A–C) and female (D–F) rats following alcohol challenge. Control, air-exposed (CON) and adolescent intermittent ethanol-exposed (AIE) rats were euthanized on PND 70–71 2 h after administration of a 4.5 g/kg ig alcohol challenge (EtOH) or equivalent volume of water (VEH), and in situ hybridization was performed to quantify Crf and Avp mRNA levels. (A) Quantification of CRF mRNA by densitometric analysis of autoradiographic signals (arbitrary units) in male rats. (B) Representative dark-field photomicrographs (100X magnification) of PVN Crf mRNA in male rats. (C) Quantification of Avp mRNA by densitometric analysis of autoradiographic signals (arbitrary units) in male rats. (D) Quantification of Crf mRNA by densitometric analysis of autoradiographic signals (arbitrary units) in female rats. (E) Representative dark-field photomicrographs (100X magnification) of PVN Avp mRNA in female rats. (F) Quantification of Avp mRNA by densitometric analysis of autoradiographic signals (arbitrary units) in female rats. Data in histograms are expressed as mean ± SEM optical density expressed percent control relative to CON/VEH average for the given experiment from 4–6 rats per treatment. * P<0.05.