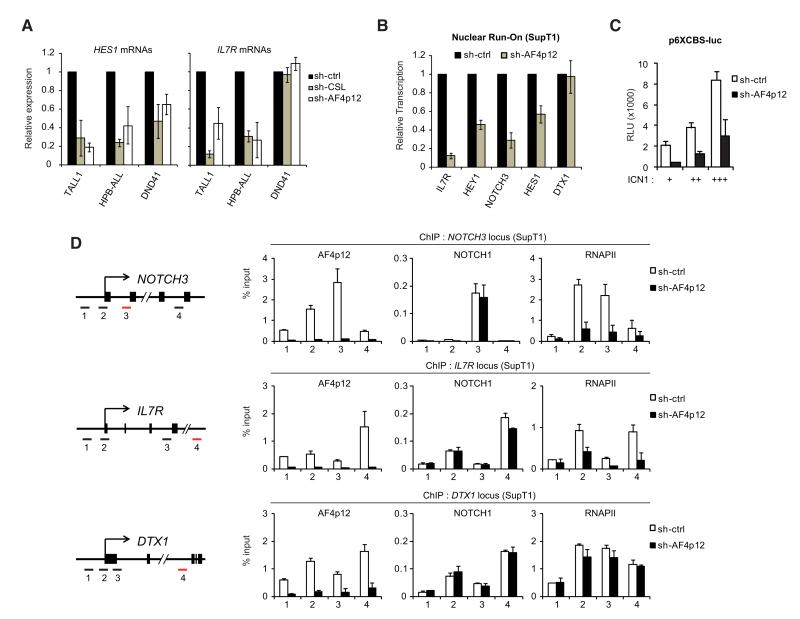
Figure 4. AF4p12 Is a Notch Transcriptional Coactivator.
(A) AF4p12 is required for Notch-target gene expression in T-ALL cell lines. TALL1, HPB-ALL, and DND41 were transduced with control, CSL or AF4p12 shRNA. Expression of HES1 and IL7R was measured by quantitative (Q-) RT-PCR (mean ± SD, n = 2). Knockdown efficiencies are shown in Figure S2D.
(B) AF4p12 affects the rate of transcription of Notch-target genes. Nuclear run-on assays (n = 3) were performed on isolated nuclei from SupT1 cells expressing control or AF4p12 shRNA. Transcripts generated during the run-on were purified using anti-BrdU beads and analyzed by Q-RT-PCR. See also Figure S3A for quantitative analysis of pre-mRNAs in AF4p12 knockdown cells.
(C) AF4p12 controls Notch transcriptional activity in transient reporter assay. HeLa cells expressing control or AF4p12 shRNA were transfected with a Notch-responsive luciferase reporter (p6XCBS-luc) and various amounts of ICN1 expression vector. The values are Relative Luciferase Units (RLU) represented as fold induction by ICN1 (mean ± SD, n = 2). Efficiency of AF4p12 knockdown is shown in Figure S3B.
(D) AF4p12 is required for RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) recruitment to Notch-target loci. ChIP assay were performed in SupT1 expressing control or AF4p12 shRNA. Results for AF4p12, NOTCH1, and RNAPII occupancy at the NOTCH3, IL7R, and DTX1 loci are shown as percentage relative to input (mean ± SD, n = 2). Numbers on the x axes represent PCR amplicons used for each locus, as depicted in the left panel.