Figure 1.
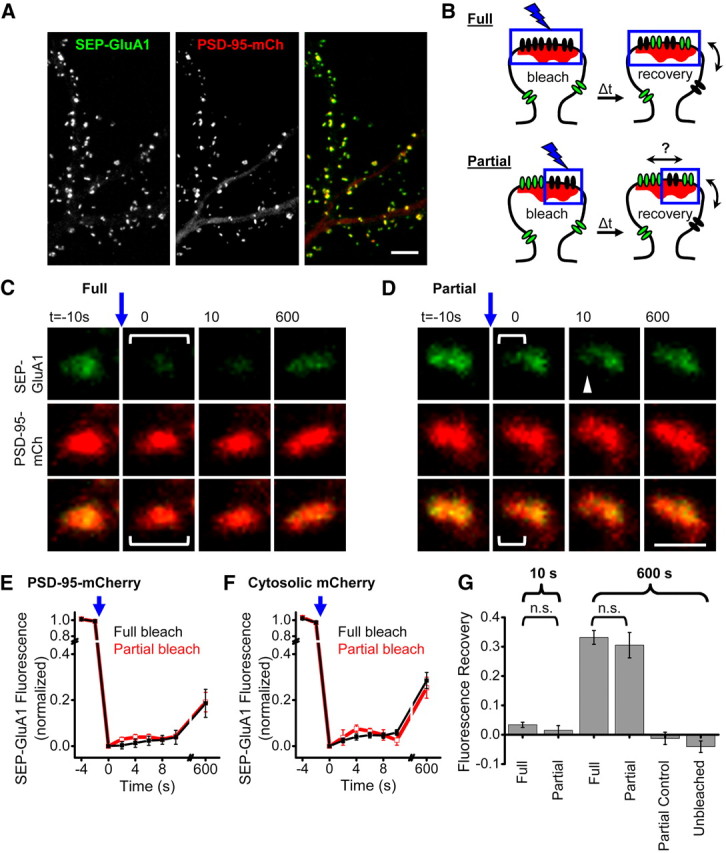
Synaptic AMPARs are confined to subsynaptic domains. A, Confocal image of cultured hippocampal neuron expressing PSD-95-mCh + SEP-GluA1. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Experimental design for comparing partial and full synapse photobleaching to measure AMPAR intrasynaptic mobility. Fully photobleached synapses (top) will only recover fluorescent receptors via exchange of extrasynaptic receptors. Partially photobleached synapses (bottom) have an additional unbleached population of receptors that will speed recovery in the bleached subregion if they are mobile. C, D, Example synapses expressing SEP-GluA1 and PSD-95-mCh where all or part of the synaptic SEP-GluA1 was photobleached. Brackets represent the region targeted for photobleaching just before t = 0. Scale bar, 1 μm. E, F, SEP-GluA1 fluorescence recovery after either full or partial synapse photobleaching. Experiments were interleaved in neurons coexpressing either PSD-95-mCh or cytosolic mCh. n = 7–19 synapses from 7 to 9 neurons. G, SEP-GluA1 fluorescence recovery in synapses targeted for full or partial synapse photobleaching, and control synaptic regions at the indicated times following photobleaching. Number of synapses/neurons: At 10 s: full 34/9, partial 20/7. At 600 s: full 37/9, partial 10/4. Unbleached region of partially bleached synapses: 10/4. Control, unbleached synapses 10/4. n.s., p ≫ 0.05.
