Figure 8.
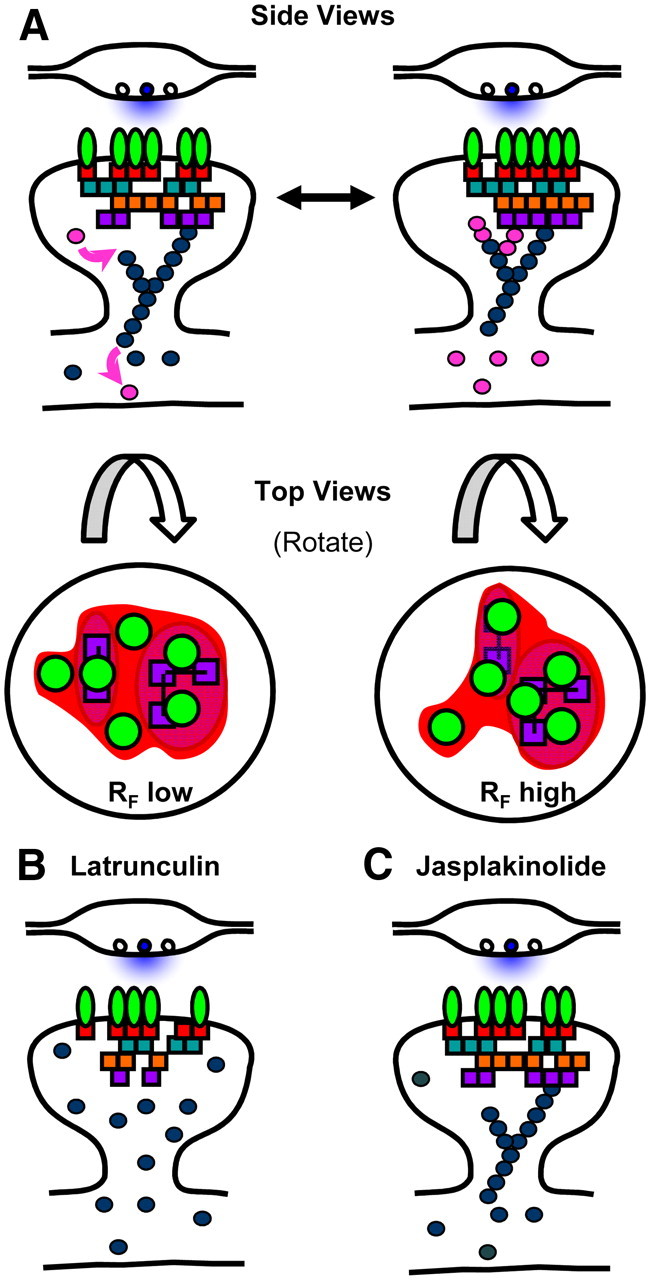
Potential mechanism of actin-regulated AMPAR subsynaptic distribution via PSD reorganization. A, A synapse viewed from the side (top) and from the top (bottom) illustrating the heterogeneous axial and lateral distribution of PSD proteins. Force generated from dynamic perisynaptic actin directly and constitutively regulates PSD lateral organization. We suspect that prolific intermolecular engagement within the PSD creates a sufficiently rigid structure to prevent mixing of PSD components over large distances. Alterations of the PSD interior in turn regulate subsynaptic AMPAR distribution, potentially by setting the position of either specific binding partners or local domains of nonspecific molecular crowding. While known binding interactions as well as the rank order of RF correlation values observed here imply a general sequence of molecular interactions that could relay information from filaments to receptors, there is not a great deal of evidence to support a specific molecular mechanism; the highly interconnected nature of PSD proteins suggests there may be many alternatives. B, Latrunculin depolymerizes spine actin filaments and at least in young neurons induces a partial loss of some PSD scaffold components. The loss of dynamic actin filaments blocks both morphology changes and subsynaptic receptor-scaffold reorganization. Receptors remain stably anchored within subsynaptic domains for long periods. While eventually the number of receptors in the synapse decreases, this is likely due to alterations in extrasynaptic receptor trafficking, not disruption of receptor stability in the synapse. C, Jasplakinolide treatment blocks synapse morphology changes and subsynaptic receptor-scaffold reorganization by preventing actin dynamics. Jasplakinolide does not strip away PSD components and does not elicit a reduction in receptor numbers, but prevents force generation and halts actin-driven reorganization of the PSD interior.
