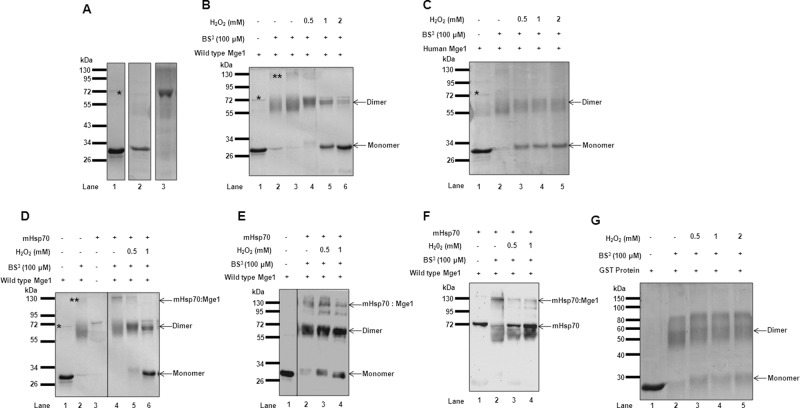
FIGURE 1:
H2O2 reduces Mge1 dimer formation and Mge1–mHsp70 complex formation. (A) Purified recombinant proteins of yeast Mge1 (lane1), human Mge1 (lane 2), and yeast mHsp70 (lane 3) were resolved on SDS–PAGE and Coomassie stained. (B) Purified recombinant yeast Mge1 (lane 1) was incubated in the presence (lanes 4–6) and absence (lanes 2 and 3) of H2O2 for 20 min at room temperature in 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and cross-linked with 100 μM BS3 (lanes 2–6) for 20 min. The cross-linking reactions were quenched, and adducts were resolved on SDS–PAGE and Coomassie stained. (C) Coomassie-stained, cross-linked adducts of human Mge1 in the presence (lanes 3–5) or absence of (lane 2) of H2O2. (D) Purified Mge1 was treated with (lanes 5 and 6) or without (lanes 1–4) increasing concentrations of H2O2 (0.5 and 1 mM) for 20 min at room temperature. The samples were incubated with purified mHsp70 (lanes 3–6) for 10 min, followed by cross-linking with BS3 (lanes 2 and 4–6) for 20 min at room temperature and were quenched with Tris-HCl buffer. The cross-linked adducts were separated on SDS–PAGE and Coomassie stained or Western transferred and probed with antibodies specific for Mge1 (E) or mHsp70 antibodies (F). (G) Purified recombinant GST protein was subjected to increasing concentrations of H2O2 and cross-linked, and cross-linked adducts were separated and stained with Coomassie. Asterisk, copurified DnaK with recombinant yeast Mge1; double asterisks, the DnaK–Mge1 complex.