Figure 1.
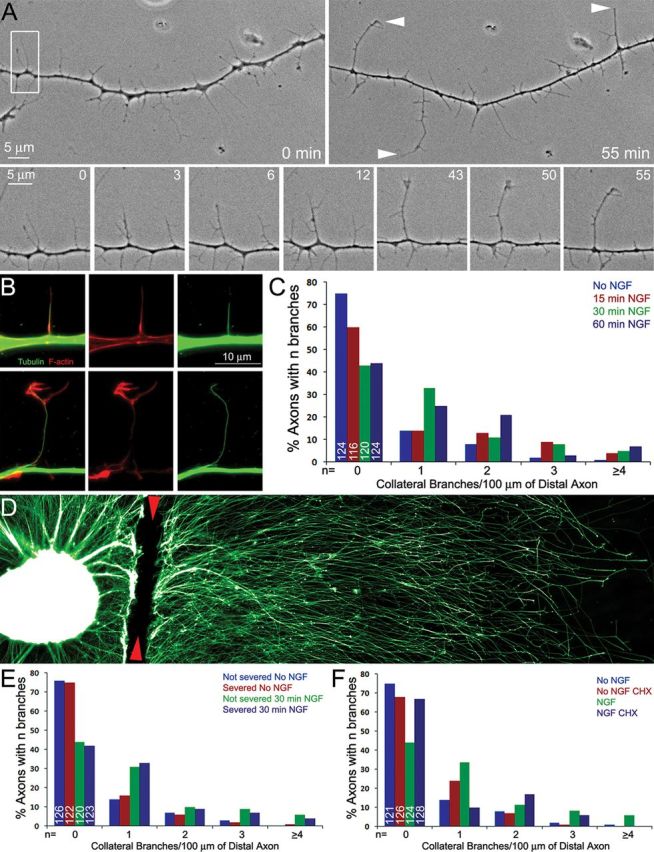
NGF induces axons branching dependent on axonal protein synthesis. A, Phase contrast time-lapse sequence of collateral formation. Top, The morphology of the axon before branch formation (0 min) and 55 min later. The arrowheads at 55 min denote structures interpreted to be collateral branches based on length and morphological criteria. Bottom, The maturation of a filopodium into a branch tipped by a dynamic small growth cone-like structure. The bottom represents the area in the white box in the top left. By 12 min the filopodium has darkened and developed an additional filopodia near its tip and other filopodia along its shaft. By 43 min the branch has extended further and developed a small growth cone. B, Examples of axons simultaneously fixed and extracted to reveal the polymeric cytoskeleton. Top, Shows an axonal filopodia invaded by a microtubule. Although a microtubule is present, the filopodium has a relatively uniform F-actin distribution and no distal accumulation of F-actin. In contrast, a mature branch contains a microtubule and a distal accumulation of F-actin (bottom). C, Distribution of the number of mature branches (0 to ≥4) along the distal 100 μm axons as a function of time after treatment with NGF. The number of axons scored per group from six separate cultures is denoted by the numbers in the 0 branches categories. In this and all subsequent experiments in this figure, the distribution of axon branches was not normal as determined by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The data are thus presented as distributions and analyzed using the χ2 tests for trend as described (see Materials and Methods). D, Example of an explant cultured in NGF and fixed immediately following severing of the axons at the base of the explant. The site of severing is denoted by the red arrowheads. The sample is stained with anti-α-tubulin. E, F, Show graphs of the number of mature branches along the distal 100 μm axons (as in C). E, Severing of the axons did not affect the ability of axons to generate mature collateral branches in response to NGF. Severed axons and non-severed axons from the same cultures were scored providing a within-sample comparison. F, Pretreatment of severed axons with CHX before axon severing impairs the ability of severed axons to generate mature collateral branches in response to NGF. CHX treatment had similar effects on non-severed axons (data not shown).
