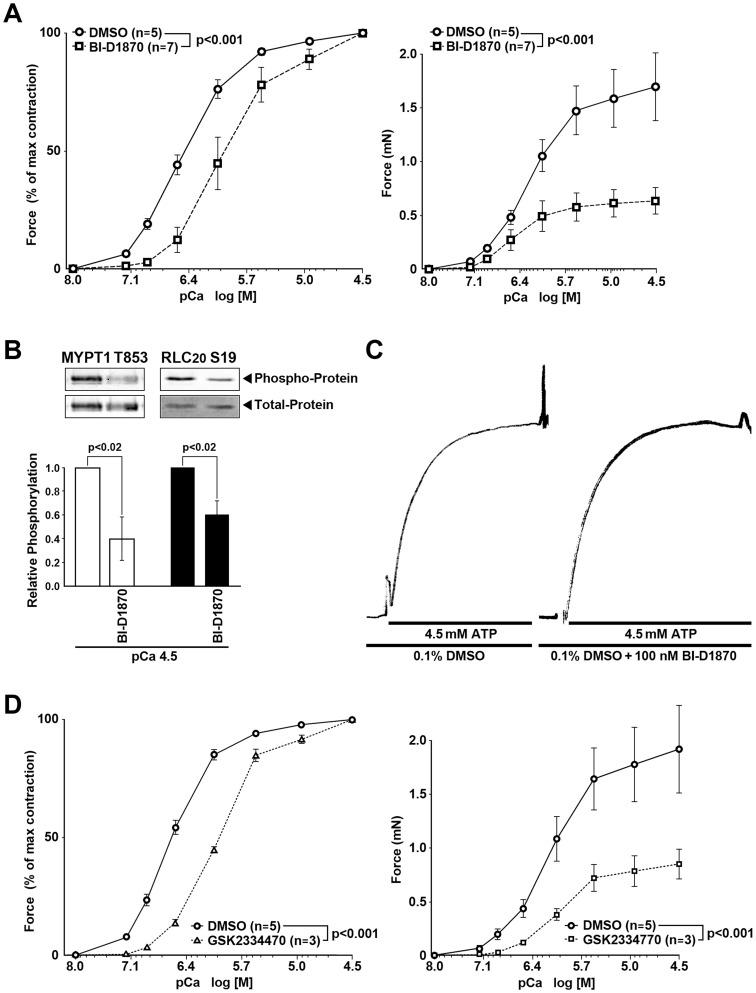
Figure 3. RSK and PDK1 contribute to Ca2+-induced force, MYPT1 and RLC20 phosphorylation in α-toxin permeabilized rabbit pulmonary artery SM.
RSK inhibitor, BI-D1870 is without effect on the actomyosin ATPase. (A) RSK inhibitor, BI-D1870 (100nM), right shifted the pCa2+-force relationship and decreased the maximal force (milli-Newtons, mN) at each intracellular Ca2+ concentration (pCa) compared to the Control diluent, DMSO. (B) BI-D1870 (100 nM) decreased phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr853 (n = 3) and RLC20 phosphorylation at Ser19 (n = 4) at maximal Ca2+-induced (pCa 4.5) force. (C) BI-D1870 (100 nM) was without effect on the ATP-induced rate of force development in Triton permeabilized mouse ileum SM with pre-thiophosphorylated light chains and depleted of ATP. T1/2 = 4.8±1.2 sec vs 5.0±1.3 sec in the Control (DMSO) vs BI-D1870 respectively, p = ns, n = 3. Thus, the inhibitor effects of BI-D18670 are not due to inhibition of the actomyosin ATPase. (D) The PDK1 kinase inhibitor GSK 2334470 (30 µM) also suppressed the pCa2+-force relationship and reduced the absolute force (mN).