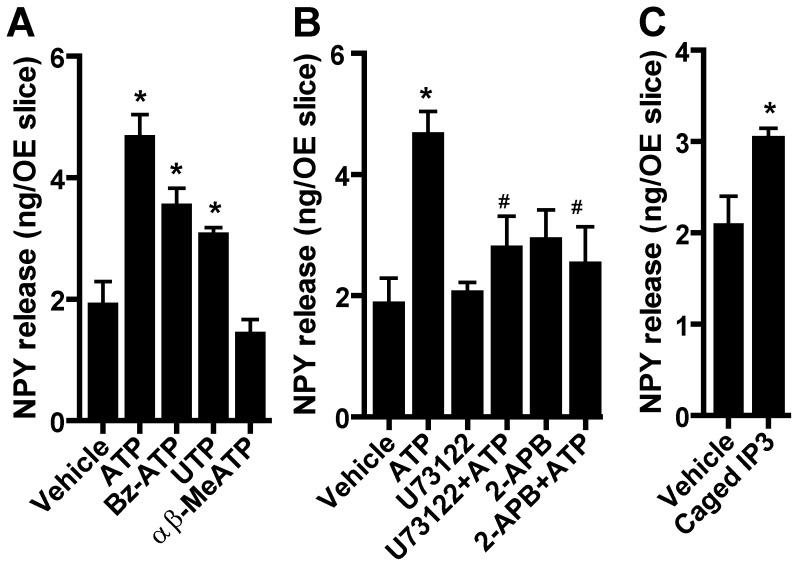
Figure 1. The release of neurotrophic factor NPY following injury simulation is mediated by a purinergic receptor, phospholipase C, and IP3/IP3 receptor pathway.
(A) P2X1,7 and P2Y2 receptors mediate NPY release. Neonatal OE slices from Swiss Webster mice were incubated with vehicle (0.2% DMSO), non-selective P2 purinergic receptor agonist (ATP, 50 µM), P2X1,7 agonist (BzATP, 50 µM), P2Y2,4,6 agonist (UTP, 50 µM) or P2X1,2/3,3 agonist (αβ-MeATP, 50 µM) for 1 hour and the levels of NPY in media were measured by ELISA. *, p<0.05 vs. vehicle (one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post-hoc test; n = 6, 4, 4, 4 and 3 replications, respectively.) (B) ATP-induced NPY release is PLC- and IP3 receptor-dependent. Neonatal OE slices from Swiss Webster mice were pre-incubated with vehicle (0.2% DMSO), PLC inhibitor (U73122, 100 µM), or IP3 receptor inhibitor (2-APB, 100 µM) for 45 min prior to addition of vehicle (0.2% DMSO) or ATP (50 µM). Media was collected after 1 hr and the levels of NPY in media were measured by ELISA. *p<0.01 vs. vehicle; #p<0.05 vs. ATP (two-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post-hoc test; n = 6, 4, 4, 4, 5 and 5 replications, respectively.) (C) IP3 induces NPY release. Neonatal OE slices from Swiss Webster mice were incubated with vehicle (0.09% pluronic acid +0.45% DMSO) or caged iso-IP3/PM (caged IP3, 1.5 µM) and slices were illuminated with unfiltered light from a xenon arc lamp (30 min) to uncage IP3. Media was collected 1 hr later and the levels of NPY were measured by ELISA. p = 0.02 (Student’s t-test; n = 3 and 4 replications.).