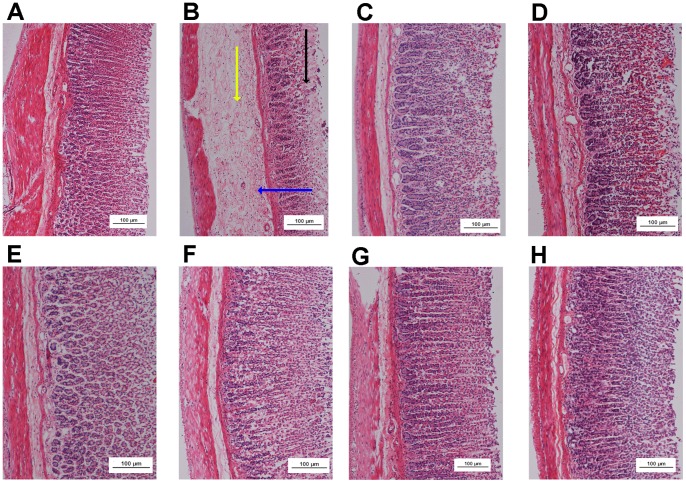
Figure 5. Histological study of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats.
In the negative control group no injuries to the gastric mucosa were observed (A). The ethanol control group showed severe disruption to the surface epithelium (black arrow), gastric lesions penetrating deeply into the mucosa, and extensive edema of the submucosal layer (yellow arrow), and leukocyte infiltration (blue arrow) was present (B). The reference control group showed mild disruption of the surface epithelium mucosa. There was edema and leukocyte infiltration of the submucosal layer (C). Group 4 (1 mg/kg AMDCP) exhibited moderate disruption of the surface epithelium. There was edema with leukocyte infiltration of the submucosal layer (D). Group 5 (5 mg/kg AMDCP) had mild disruption of the surface epithelium. There was no edema or leukocyte infiltration of the submucosal layer (E). Groups 6, 7 and 8 (10, 15 and 20 mg/kg AMDCP, respectively) did not show any disruption to the surface epithelium. There was no edema or leukocyte infiltration of the submucosal layer (F, G and H) (H & E stain, 10x).