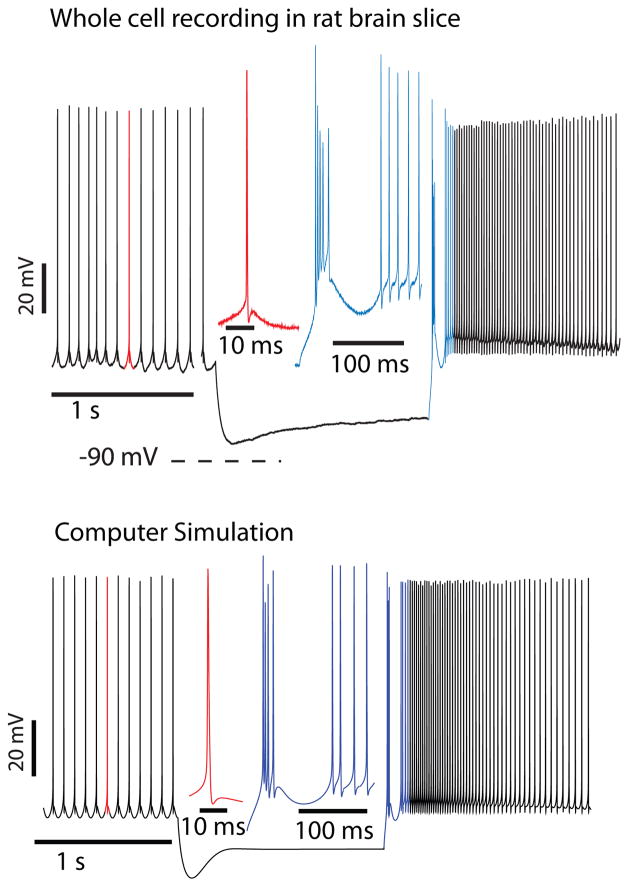
Figure 2.
Rebound response in CN neurons (adapted from Steuber et. al., 2011). Top panel: Response of a CN neuron in a brain slice recording to a 1.5 s current injection of −150 pA. Two clear components of the strong rebound response can be discriminated: a fast spike burst, and a prolonged period of spike rate acceleration. Bottom Panel: The computer model can reproduce these rebound components through the activation of T-type calcium current for the fast rebound burst and persistent sodium current for the slow rebound period. These currents are de-inactivated during the period of hyperpolarization, and the depth and duration of hyperpolarization determine the intensity of each rebound component (see Steuber et al, 2011 for details).