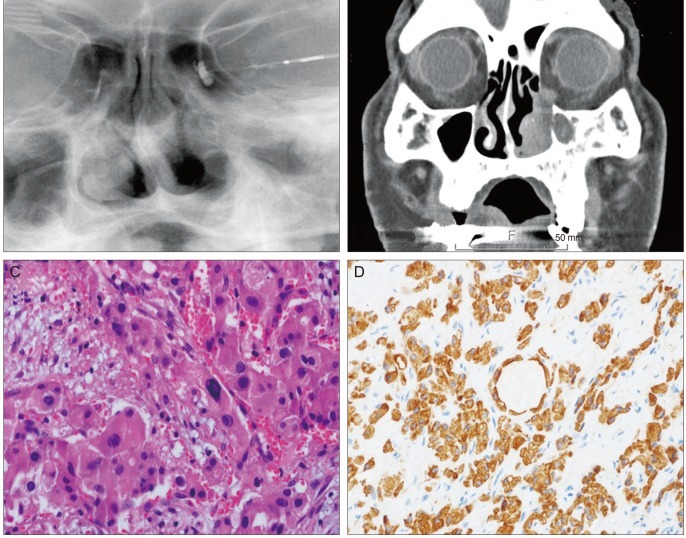
Fig. 1.
(A) Left dacryocystography demonstrates nasolacrimal duct obstruction. (B) Computed tomography revealed that the tumor in the left nasal cavity extended to the nasolacrimal duct and sac, and that the mass did not extend into the orbit. (C) Histological examination of the tumor revealed an oncocytic carcinoma; a destructive, infiltrating pattern and tumor cells composed of eccentrically located nuclei with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (hematoxylin-eosin, ×400). (D) Pancytokeratin is strongly positive in tumor cells.