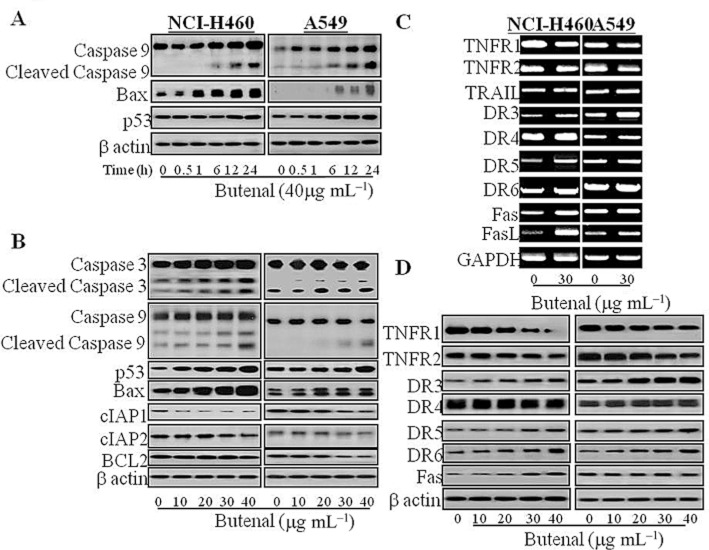
Figure 2.
Effect of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal on the expression of apoptosis regulatory proteins. (A) The cells were treated with same concentration (40 μg·mL−1) of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal and harvested at different time points. (B) The cells were treated with different concentrations (0–40 μg·mL−1) of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal at 37°C for 12 h. Equal amounts of total proteins (50 μg per lane) were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE. Expressions of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, p53, Bax, cIAP1/2, Bcl-2 and β-actin were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. β-Actin protein was used an internal control in NCI-H460 and A549 lung cancer cells. Each band is representative of three independent experiments. (C) Effect of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal on death receptor expression in NSCLC cell lines. The cells were treated with different concentrations (0–40 μg·mL−1) of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal at 37°C, and total RNA were extracted and examined for expressions of TNFRSF1A and 1B, TNF-R1 and 2, FAS, TNFRSF12, 10A, 10B and 21 (DR-3, -4, -5, -6) and GAPDH by RT-PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control to show equal RNA loading. Equal amounts of total proteins (50 μg·per lane) were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE. Expressions of TNFRSFs, FAS, and β-actin were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. β-Actin protein was used an internal control. Each band is representative for three experiments.