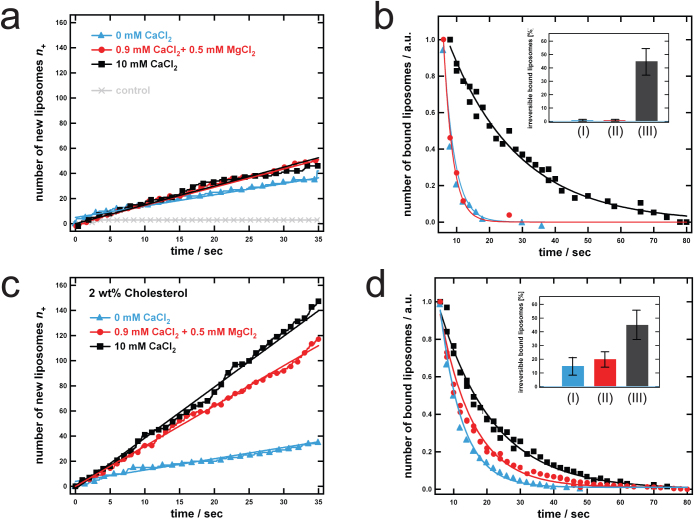
Figure 2. Bivalent cations and cholesterol modulate association and dissociation of Lex-Lex interaction.
(a) and (b) Number of newly arrived liposomes n+ as a function of time and (c) and (d) normalized number of liposomes that are still bound as a function of time for the different buffers used: TRIS buffer without additional cations (blue), TRIS buffer containing 0.9 mM CaCl2 and 0.5 mM MgCl2 (red) and TRIS buffer containing 10 mM CaCl2 (black) and the control (grey). (a) and (b) SLBs are composed of 95 wt% POPC + 5 wt% Lex GSL and liposomes of 94 wt% POPC + 5 wt% Lex GSL + 1wt% Rhod-PE. For the control Lex GSL was replaced by Lea GSL. (c) and (d) SLBs are composed of 93 wt% POPC + 5 wt% Lex GSL + 2 wt% cholesterol and liposomes of 94 wt% POPC + 5 wt% Lex GSL + 1 wt% Rhod-PE. Continuous lines represent the corresponding curve fits. Inset (b) and (d): Fraction of irreversible bound liposomes during the time of an experiment for (I) TRIS buffer without additional cations (blue), (II) TRIS buffer containing 0.9 mM CaCl2 and 0.5 mM MgCl2 (red) and (III) TRIS buffer containing 10 mM CaCl2 (black).