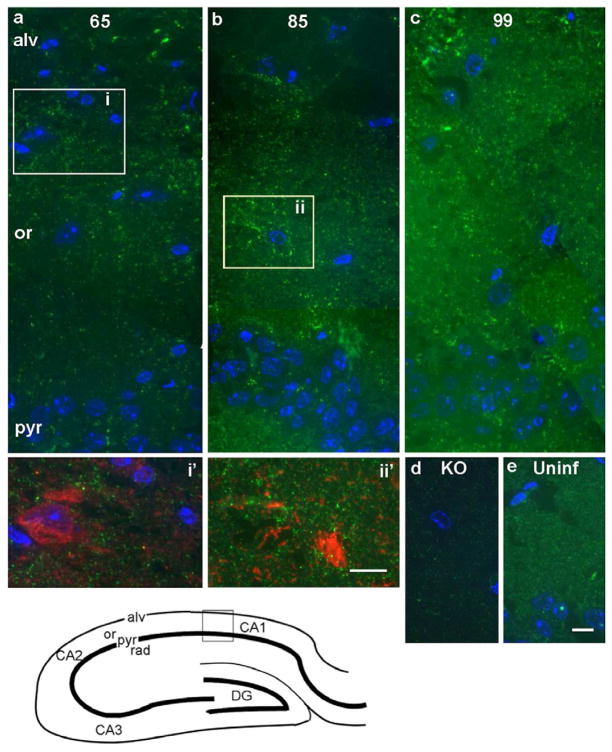
Figure 2. Saf32 immunofluorescence labeling of PrP in the hippocampal CA1 region.
Bottom left, a diagram of the hippocampus, with the area shown in (a–e) indicated by the box. (a–c) Composite images of prion-infected hippocampus at 65 dpi (a), 85 dpi (b) and 99 dpi (c). In (a) an area of higher labeling in the stratum oriens (boxed area i), is shown at higher magnification in i′, double-labeled with Saf32 (green) and anti-GABA (red). Co-labeling was not apparent. Patches of bright labeling are also visible in the alveus. In (b), area equivalent to box ii from a serial section, double-labeled with Saf32 (green) and anti-glutamine synthetase (red) is shown in ii′. Again, little co-labeling is evident. (d, e) As controls, hippocampal sections taken from a PrP-deficient mouse (KO; d) and an uninfected FVB mouse (Uninf; e). Saf32 gives an evenly distributed ‘granular’ pattern of labeling in the uninfected hippocampus (e). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue) in (a–e). Abbreviations: pyr, pyramidal layer; or, stratum oriens; alv, alveus; KO, Prnp0/0; CA1, CA2, CA3, regions of the hippocampus; DG, dentate gyrus. Bars represent 10 μm; bar in (e) also applies to (a–d).