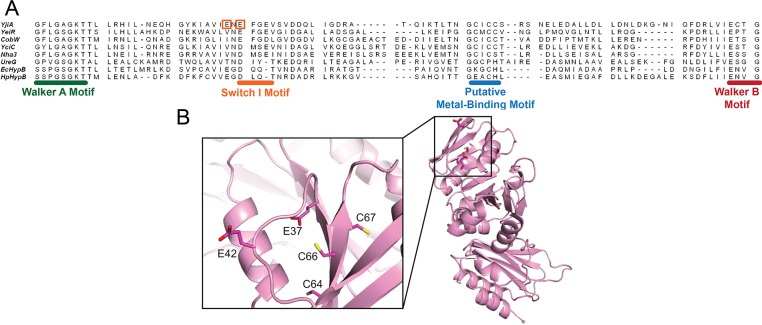
Figure 3.
Structure of WT YjiA and location of the metal-binding site in the primary structure of the GTPase domain. (A) Sequence alignment of the GTPase domain regions between the Walker A and Walker B motifs of representative G3E GTPases generated by the COBALT sequence alignment program (available online at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/cobalt/).65 Located between the Walker A and B motifs is a putative metal-binding motif, the location of which is common among the G3E GTPases. The two glutamates mutated in this study are highlighted by orange boxes. The species from which the protein sequences were derived and the starting sequence positions (in brackets) are as follows: YjiA, E. coli (11); YeiR, E. coli (9); CobW, P. denitrificans (18); YciC, B. subtilis (11); Nha3, Rhodococcus sp. N-771 (13); UreG, Klebsiella aerogenes (14); EcHypB, E. coli (111); HpHypB, Helicobacter pylori (53). (B) The structure of apo-YjiA (PDB entry 1NIJ), previously published,17 features two domains. The N-terminal GTPase domain possesses a typical G3E GTPase fold with a central β-sheet core surrounded by α-helices. Located on one of the central β-strands is the conserved C64XCC67 motif. Glu37 and Glu42 are near this motif (inset).