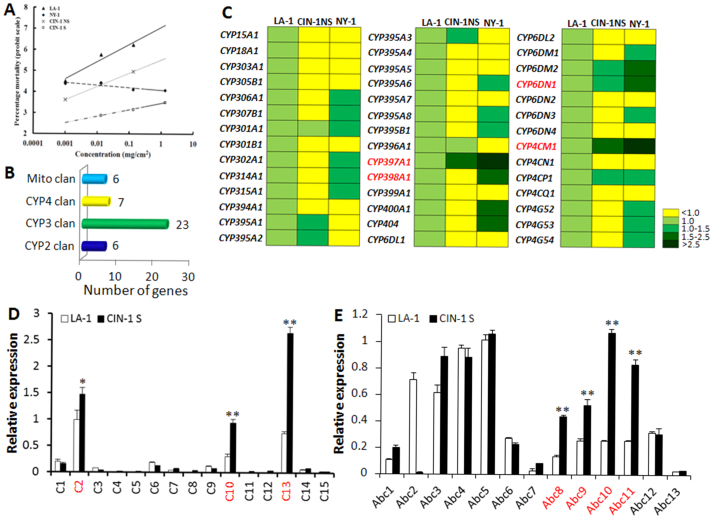
Figure 1. Identification of target genes associated with insecticide resistance.
(A) Dose-response curves (log dose versus mortality on a probit scale) for C. lectularius female adults exposed to deltamethrin. LA-1 ( ), a susceptible strain; NY-1 (
), a susceptible strain; NY-1 ( ), a deltamethrin resistant strain; CIN-1 NS (x), a deltamethrin resistant strain without selection; and CIN-1 S (
), a deltamethrin resistant strain; CIN-1 NS (x), a deltamethrin resistant strain without selection; and CIN-1 S ( ), a deltamethrin resistant strain after selection were exposed to serially diluted deltamethrin and the mortality was recorded and graphed. (B) Cytochrome P450 genes in C. lectularius. Totally 42 Cytochrome P450 genes (P450s) were identified through assembling of Cimex transcriptome and named by the P450 nomenclature committee. These genes fall into 4 clans, Mito CYP clan, CYP4 clan, CYP3 clan, and CYP2 clan. The number of P450s in each clan was labeled on the top of the column. (C) mRNA levels of 42 C. lectularius P450s in LA-1, CIN-1 NS, and NY-1. mRNA levels were shown as mean fold relative to their levels in LA-1. P450s highlighted in red showed the significant increase in CIN-1 NS and/or NY-1 compared to their levels in LA-1 (Student t-test, P < 0.05). (D) Relative mRNA levels of cuticular protein genes. Total RNAs were extracted from one week-old female adults were used in qRT-PCR to quantify relative mRNA levels in susceptible LA-1 as compared with the pyrethroid-resistant CIN-1 S. The data shown are mean + SEM (n = 3). Genes highlighted in red showed significant difference between LA-1 and CIN-1 S (Student's t test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01). (E) Same as B except the mRNA levels of Abc transporter genes were quantified.
), a deltamethrin resistant strain after selection were exposed to serially diluted deltamethrin and the mortality was recorded and graphed. (B) Cytochrome P450 genes in C. lectularius. Totally 42 Cytochrome P450 genes (P450s) were identified through assembling of Cimex transcriptome and named by the P450 nomenclature committee. These genes fall into 4 clans, Mito CYP clan, CYP4 clan, CYP3 clan, and CYP2 clan. The number of P450s in each clan was labeled on the top of the column. (C) mRNA levels of 42 C. lectularius P450s in LA-1, CIN-1 NS, and NY-1. mRNA levels were shown as mean fold relative to their levels in LA-1. P450s highlighted in red showed the significant increase in CIN-1 NS and/or NY-1 compared to their levels in LA-1 (Student t-test, P < 0.05). (D) Relative mRNA levels of cuticular protein genes. Total RNAs were extracted from one week-old female adults were used in qRT-PCR to quantify relative mRNA levels in susceptible LA-1 as compared with the pyrethroid-resistant CIN-1 S. The data shown are mean + SEM (n = 3). Genes highlighted in red showed significant difference between LA-1 and CIN-1 S (Student's t test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01). (E) Same as B except the mRNA levels of Abc transporter genes were quantified.