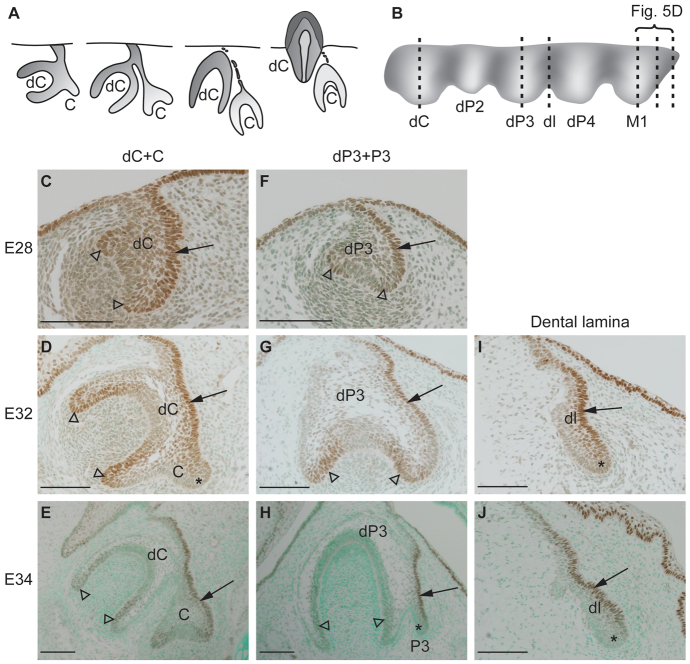
Fig. 3.
Sox2 expression localizes to dental lamina and successional dental lamina during ferret tooth replacement. (A) Schematic of frontal sections showing development of the ferret permanent canine (C), which will later replace the deciduous canine (dC). (B) Schematic sagittal and buccal view of the developing ferret tooth row showing the deciduous canine (dC), deciduous second (dP2), third (dP3) and fourth premolar (dP4), and first molar (M1) connected by the dental lamina (dl). Dashed lines in B indicate the sites of sections in C-E (dC), F-H (dP3) and I,J (dl) and in Fig. 5D (M1). (C-J) Localization of Sox2 protein (brown) during ferret tooth replacement. Arrows point to Sox2 expression in lingual dental epithelium. Asterisks indicate the Sox2-negative free end in the successional dental lamina, and in the dental lamina between deciduous teeth. Sox2 localizes also to the cervical loops and inner enamel epithelium (C-H, arrowheads). A and C-J are frontal sections, lingual to the right; B is a sagittal view, posterior to the right. Scale bars: 100 μm.