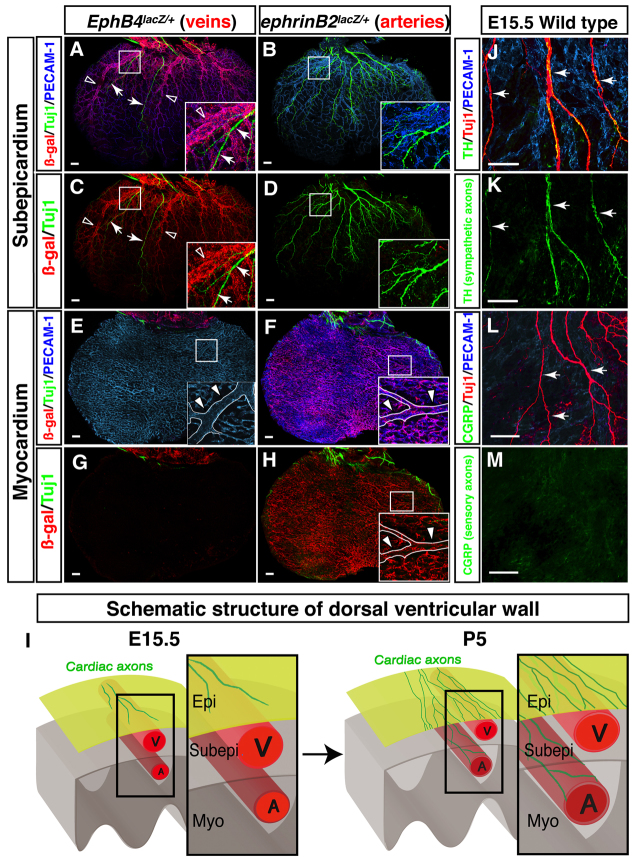
Fig. 2.
Cardiac sympathetic axons associate with large diameter coronary veins within the subepicardial layer of the dorsal ventricular wall. (A-H) The dorsal ventricular walls of E15.5 EphB4taulacZ/+ (A,C,E,G; the venous marker EPHB4) or ephrinB2taulacZ/+ (B,D,F,H; the arterial marker ephrin B2) hearts are shown. Whole-mount triple immunofluorescence confocal microscopy was performed with antibodies to PECAM1 (A,B,E,F, blue), TUJ1 (A-H, green) and β-galactosidase (A-H, red). Boxed regions in A-F,H are magnified in insets. (A-D) The subepicardium. Coronary veins expressing EphB4taulacZ are clearly visible in EphB4taulacZ/+ embryos (A,C). However, arteries expressing ephrinB2taulacZ are barely detectable in ephrinB2taulacZ/+ embryos (B,D). TUJ1+ cardiac axons (A,C, arrows) associate with EPHB4+ large diameter veins (A,C, open arrowheads). (E-H) The myocardium. Coronary arteries expressing ephrinB2taulacZ cover the deeper layer in ephrinB2taulacZ/+ embryos (F,H). One large diameter artery runs from the base towards the apex of the ventricle (E,F,H, insets, arrowheads). EphB4taulacZ-expressing veins are barely detectable in EphB4taulacZ/+ embryos (E,G). TUJ1+ cardiac axons are also not detected in the myocardial layer (E-H). (I) Schematic illustrating sympathetic innervation of the developing heart. By E15.5, coronary veins develop to form large diameter branches within the subepicardial layer (Subepi), where cardiac axons initiate distal axon extension. Coronary arteries develop separately, in the myocardial layer (Myo). By P5, cardiac axons extend into the myocardial layer (see supplementary material Fig. S2). These axons innervate large diameter coronary arteries as final targets. Epi, epicardial layer; V, vein; A, artery. (J-M) Neuronal subtype characterization. E15.5 hearts were labeled with antibodies to the sympathetic neuron marker tyrosine hydroxylase (TH; J,K, green) or the sensory neuron marker calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP; L,M, green) in addition to PECAM1 (J,L, blue) and TUJ1 (J,L, red). TUJ1+ nerves are mostly TH+, indicating that these axons in the subepicardium are mostly sympathetic nerves (J,K, arrows). CGRP+ sensory innervation is not detectable at E15.5 (L,M, arrows). Scale bars: 100 μm.