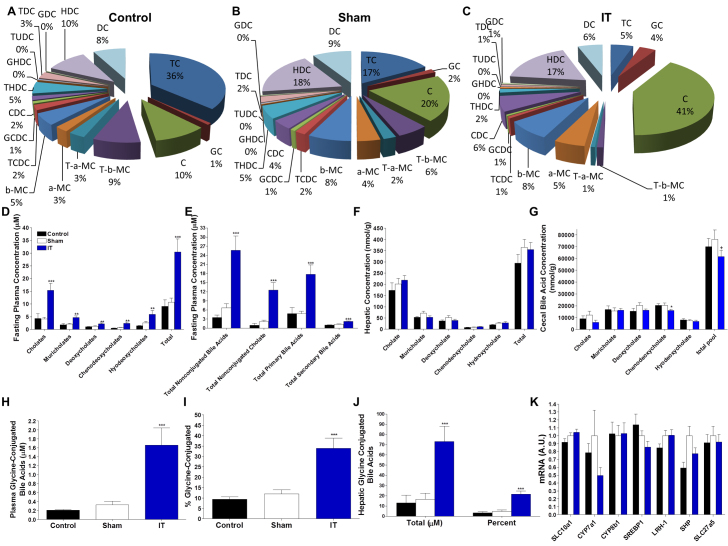
Fig. 5.
IT surgery preferentially increases nonconjugated primary bile acids. (A-C) Fasting plasma bile acid profiles in control (A), sham (B) and IT-operated animals (C) at 2 months after surgery. (D) Fasting plasma bile acid concentrations. (E) Fasting plasma non-conjugated bile acid, non-conjugated cholic acid, primary bile acid and secondary bile acid concentrations. (F) Hepatic bile acid profiles. (G) Bile acid profiles in cecal contents. (H) Fasting plasma glycine-conjugated bile acid concentrations. (I) Fasting plasma glycine-conjugated bile acid concentrations expressed as a percentage of conjugated bile acids. (J) Hepatic glycine-conjugated bile acid concentrations expressed as an absolute value and as a percentage of the total hepatic bile acid pool. (K) Hepatic mRNA expression of genes involved in bile acid metabolism and the FXR pathway relative to ARBP. All plasma values were measured at 2 months after surgery. Liver and cecal contents values were measured at 4.5 months after surgery; n=16 per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 for IT compared with control and sham, +P<0.05 compared with sham by Student's t-test. C, cholate; CDC, chenodeoxycholate; DCA, deoxycholate; GC, glycocholate; GCDC, glycochenodeoxycholate; GDC, glycodeoxycholate; GHDC, glycohyodeoxycholate; HDC, hyodeoxycholate; T-a-MC, tauro-α-muricholate; T-b-MC, tauro-β-muricholate; TC, taurocholate; TCDC, taurochenodeoxycholate; TDC, taurodeoxycholate; THDC, taurohyodeoxycholate; TTHC, taurotetrahyodeoxycholate; TUDC, tauroursodeoxycholate.