Fig. 1.
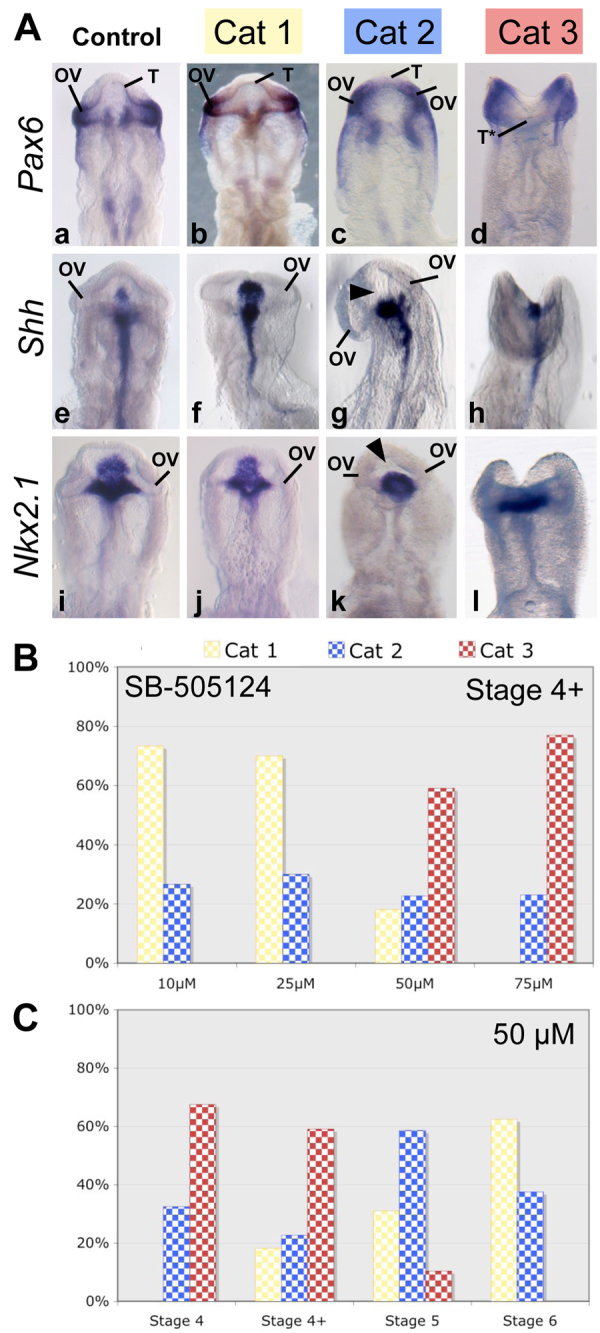
NODAL signal inhibition by SB-505124 treatment leads to severe forebrain defects; the dose-response relationship is nonlinear. (A) Ventral views of chick embryo heads at stage 12. Control embryos (n=150) were treated with DMSO (Aa, Ae, Ai). Other embryos were treated with one of a series of SB-505124 concentrations (10-75 μM) between stage 4 and stage 6 (n=317). Resulting phenotypes were classified into three categories according to morphology and in situ hybridization for Pax6 (n=111) (Aa-Ad), Shh (n=107) (Ae-Ah) and Nkx2.1 (n=99) (Ai-Al). The order of increasing severity was: category 1, category 2 and category 3. Arrowheads show the downregulation of Shh (Ag) and Nkx2-1 (Ak) expression in the ventral forebrain. (B) Distribution of the phenotypes of stage 4+ embryos treated with one of a series of SB-505124 concentrations: 10 μM (n=15), 25 μM (n=20), 50 μM (n=22) or 75 μM (n=26). (C) Distribution of the phenotypes of embryos treated with 50 μM SB-505124 starting at various stages: from stage 4 (n=40), stage 4+ (n=22), stage 5 (n=29) and stage 6 (n=16). OV, optic vesicles; T, telencephalon; T*, non-fused telencephalon; Cat, category.
