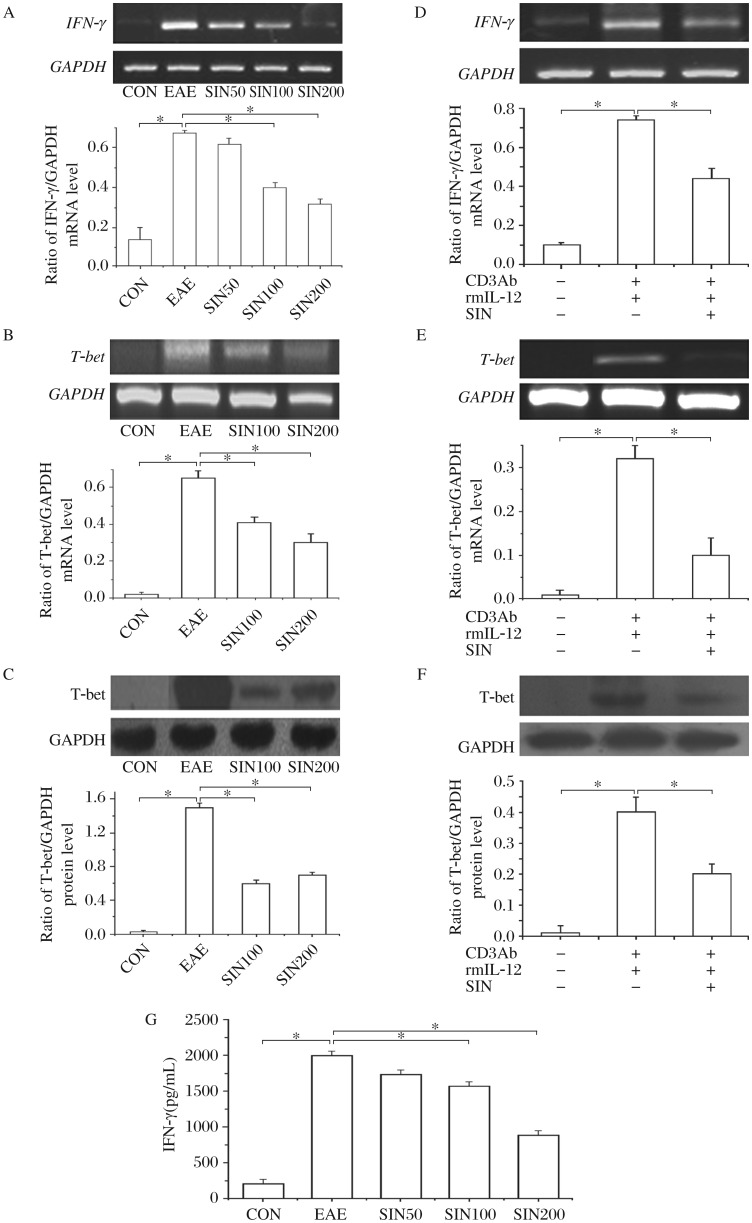
Fig. 4. Sinomenine decreases the levels of IFN-γ and T-bet in the spinal cords of EAE rats and primary splenocytes.
Cytokine levels in the spinal cords from EAE animals with and without sinomenine (SIN) treatment (n = 6 per group) were analyzed at d 4 post-onset. IFN-γ mRNA (A, product is 353 bp with 421 pb GAPD as internal control) and T-bet mRNA (B, product is 274 bp with 421 pb GAPD as internal control) levels were determined by RT-PCR, and T-bet protein levels (C) were quantified by Western blotting, and IFN-γ levels by ELISA (G). The results shown are mean±SD for three independent experiments. Primary splenocytes from Sprague Dawley (n = 6) were cultured with the stimulation of anti-CD3 antibody and IL-12, in the presence or absence of SIN (1 mmol/L). After 24 h, the cells were harvested and analyzed for IFN-γ (D, product is 353 bp with 421 pb GAPD as internal control) and T-bet mRNA (E, product is 274 bp with 421 pb GAPD as internal control). After 48 h, cells were harvested and analyzed for T-bet protein (F). *P < 0.05.