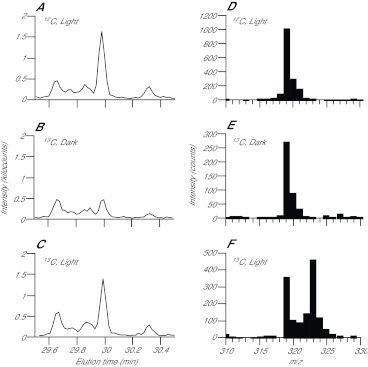
Fig. 2.
GC-MS identification of photosynthetically produced glucose and of a glucose fragment useful in quantitating the incorporation of 13C into newly synthesized glucose. CC7 anemones were incubated with 10 mg ml−1 12C-bicarbonate in the light for 10 min (A,D), with 10 mg ml−1 13C-bicarbonate in the dark for 10 min (B,E) or with 10 mg ml−1 13C-bicarbonate in the light for 10 min (C,F), and homogenates were prepared and analyzed as described in the Materials and methods. (A–C) Chromatograms produced by summing the MS peak intensities from 310 to 330 m/z for each elution time shown, showing a peak identified as glucose by comparing its elution time and MS spectrum (shown in part in D–F) to those observed in previous work and in our own glucose-standard runs (supplementary material Fig. S2). (D–F) Portions of the MS spectrum (m/z 310–330) of the material eluting from the GC at 29.95 min. Note that the m/z values are those for the derivatized glucose fragment; the rightward tail on each peak is due to naturally occurring 13C (~1.1%) and the isotopic distribution of the silicon in the silate groups used for derivatization (see supplementary material Fig. S2 legend for more details).