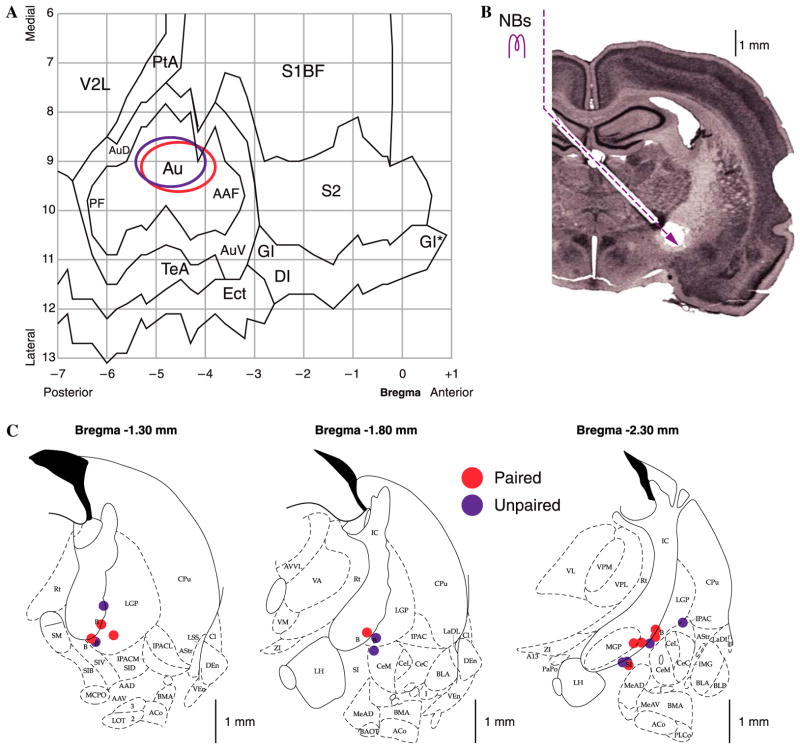
Fig. 4.
Location of electrodes. Cortical recording sites and NB stimulation sites. (A) EEG recording loci. The ovals indicate the location of epidural recordings based on their stereotaxic coordinates using a cortical map derived from Paxinos and Watson (1997). Sites for paired and unpaired groups were over primary auditory cortex and overlapped. (B) Nissl section showing the placement of stimulating electrodes in the nucleus basalis by a contralateral approach, to avoid damage to ipsilateral structures. (C) Diagrams of three coronal sections showing the NB stimulation sites. Paired and unpaired group sites were intermingled. Abbreviations: B, basal nucleus of Meynert; CeM, amygdala central nucleus medial; CeL, amygdala central nucleus lateral; CPu, caudate–putamen; IC, internal capsule; IPAC, interstitial nucleus of posterior limb of anterior commissure; LGP, lateral globus pallidus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; SI, substantia innominata; SIB, substantia innominata, basal; SIV, substantia innominata, ventral; Au, primary auditory cortex; AAF, anterior auditory field; AuD, secondary auditory cortex, dorsal; AuV, secondary auditory cortex, ventral; PF, posterior auditory field; S1BF, primary somatosensory cortex, barrel field; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; TeA, temporal association cortex; V2L, secondary visual cortex, lateral area.