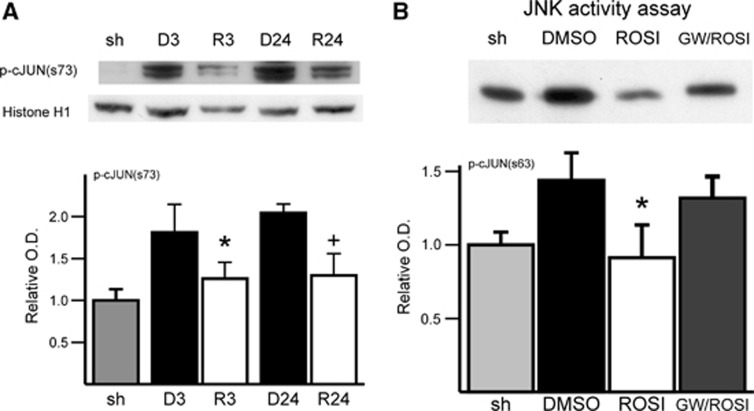
Figure 4.
Rosiglitazone treatment attenuated increased phosphorylation of c-Jun (p-cJun) in the nuclear fraction after middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion after 3 and 24 hours of reperfusion. (A) Western blot and densitometric analysis of p-cJun (s73) and histone H1 expression (n=4 each group, *P<0.05 versus 3 hours of reperfusion with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) treatment, +P<0.05 versus 24 hours of reperfusion with DMSO treatment). (B) Representative blot of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity assay where p-cJun by JNK was measured. The p-cJun band represents relative JNK activity precipitated by cJun fusion proteins. c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity induced by MCA occlusion and 3 hours of reperfusion was ameliorated with rosiglitazone treatment. The effect of rosiglitazone was reversed by GW9662 treatment (n=4 each group, *P<0.05 versus DMSO treatment group). GW, GW9662; O.D., optical density; ROSI, rosiglitazone; sh, sham.