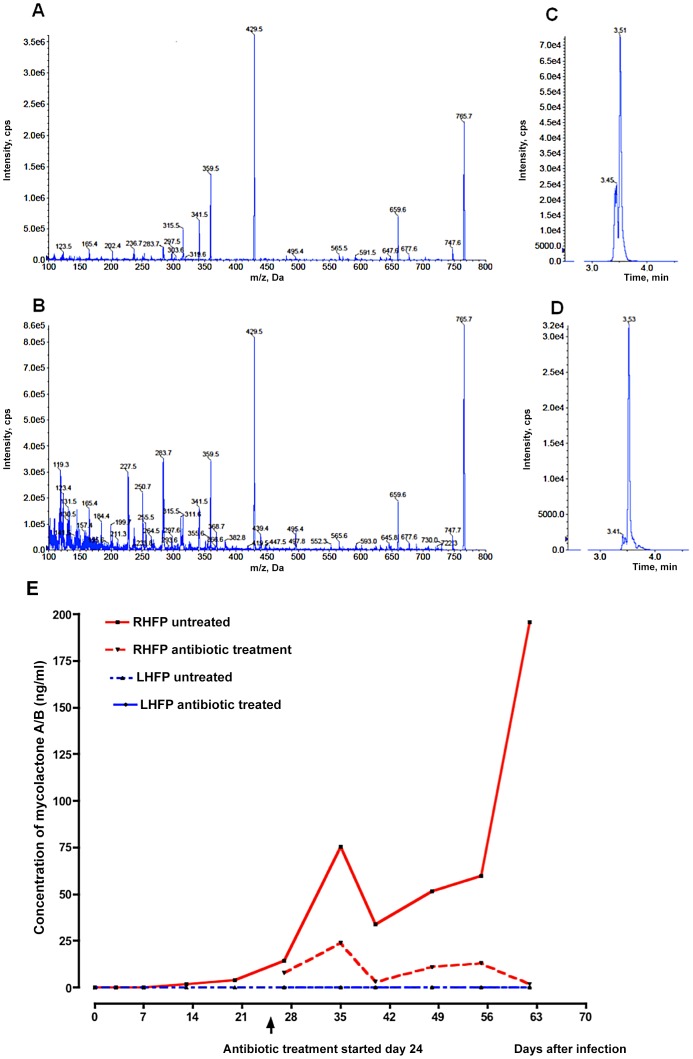
Figure 6. Mycolactone detection by mass spectrometry in mouse footpads.
A. EPI Mass spectra indicated a propensity of authentic mycolactone A/B to form a sodium adduct (m/z 765.7, [M+Na+]). Fragment ions at m/z 429.6 and 359.5 correspond to the core lactone and polyketide side chains, respectively. B. Mycolactone A/B detected in footpad extracts displayed similar mass spectra and also contained a number of other ions (e.g. m/z 659.6 and 747.7) that were present in authentic reference material. C and D. Extracted ion chromatograms (XIC) for m/z 429.6, which was selected for quantification in LC-MRM analyses of tissue extracts. Standard mycolactone is shown in C and a footpad sample in D. The sensitivity of the assay (<10 pg) was such that it was possible to measure mycolactone in the tissue samples. E. Mycolactone (ML) was detectable as early as day 13 after infection and before the onset of visible swelling in mouse footpads. No ML was detectable in the contralateral footpad of either the RIF-STR-treated or the untreated control mice. Data based on pooled lipid extracts from 3 mice per group per time point.