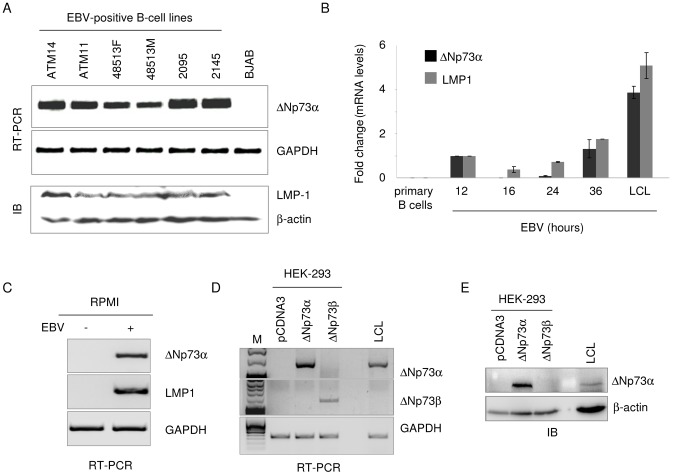
Figure 1. EBV induces ΔNp73 transcriptional activation in B cells.
(A) EBV positive and negative immortalized B cells were collected and processed for total RNA and protein extraction. The levels of ΔNp73 and GAPDH were determined by RT-PCR (upper panels). Protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (lower panel). (B) Primary B cells were infected with EBV-GFP recombinant virus. Infected cells were collected at the indicated time points and processed for RNA extraction. The levels of ΔNp73, LMP-1 and GAPDH were determined by quatitative RT-PCR. The data are the mean of three independent experiments. (C) RPMI cells were infected with EBV and 2 weeks after infection were collected and processed for RNA extraction and RT-PCR analysis. (D) Total RNA was prepared from LCL and HEK 293 cells transduced with empty retrovirus or expressing ΔNp73α or ΔNp73β isoform RT-PCR was performed using specific ΔNp73 isoform primers. M indicates the DNA marker used to confirm the size of the PCR fragments (MassRuler DNA Ladder Mix, Fermentas). (E) Whole cell extracts were prepared from LCL and HEK293 cells, the latter were transfected with pcDNA empty or with pcDNA- ΔNp73α and ΔNp73β. 40 µg of cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with p73 or β-actin antibody.