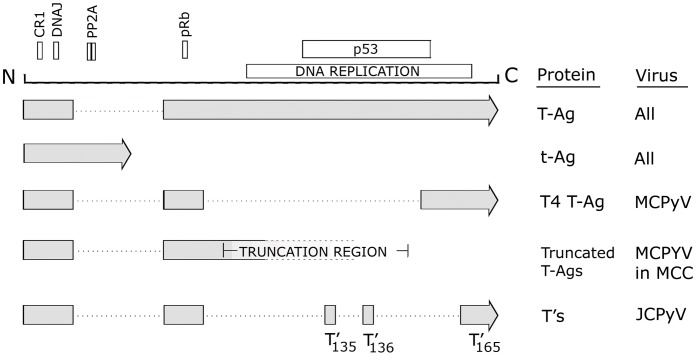
Figure 2. Transforming proteins produced by the early region of human polyomaviruses.
A schematic of the early region of human polyomaviruses showing the various protein motifs including conserved region 1 (CR1), the DNAJ domain, the protein phosphatase-2A binding site, the retinoblastoma protein binding site, the region involved in DNA replication, and the p53 binding site. All 10 HPyV produce large T-antigen (T-Ag) and small t-antigen (t-Ag). In addition, MCPyV and JCPyV produce additional splice variants, T4 and the T's, respectively. In Merkel call carcinoma, MCPyV is found integrated in such a way as to cause targeted disruption of T-Ag as indicated by the labeled “truncation region,” which was defined by sequencing the T-Ag genes from multiple MCC (22). Note that truncation at this region preserves the pRb site but not the p53 site or DNA replication region as discussed in the text. The 17kT variants of BKPyV and MCPyV are not shown.