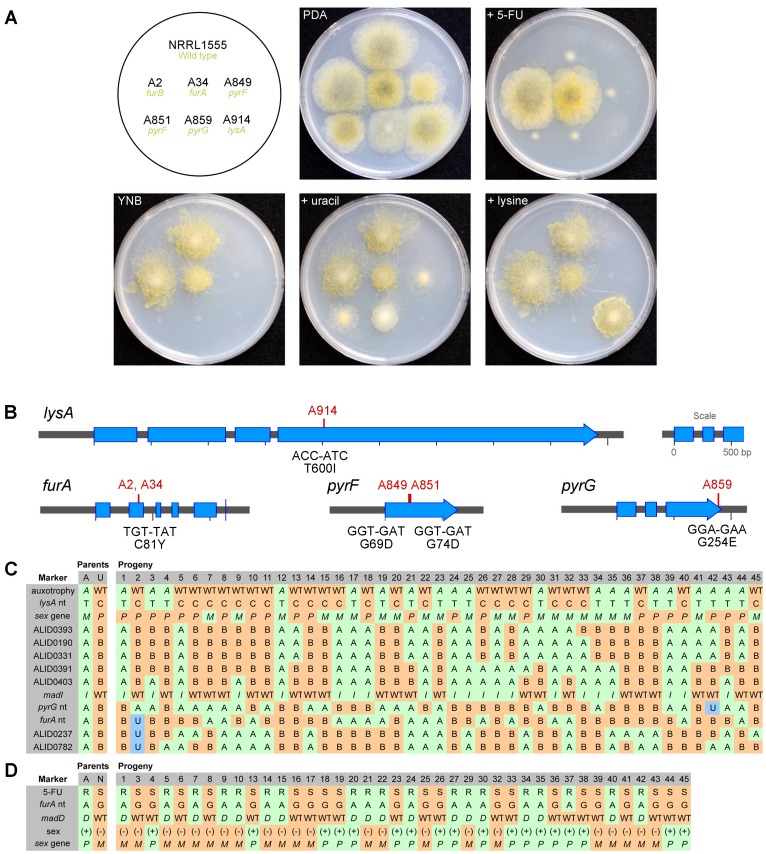
Figure 3. Mutations identified in strains of Phycomyces.
A. Phenotypes on potato dextrose agar (PDA), PDA +250 mg/L 5-fluorouracil, YNB minimal medium, and YNB supplemented with uracil (20 mg/L) or lysine (30 mg/L) after three days growth at room temperature. The PDA was supplemented with uracil to support growth of the pyrF and pyrG mutants. B. The positions (red lines and strain names) and nature (codons and amino acid residue substitutions) of the mutations in the corresponding genes in these strains. C. Segregation data for lysA. Parents were A914 (A) and for UBC21 (U). Alleles are: for auxotrophy are either A for lysA or WT for wild type, the C or T nucleotide in the lysA gene, for PCR-RFLPs A for NRRL1555 and B UBC21, the sex gene is either sexM (M) or sexP (P), and the phototropism phenotype I for madI or WT for wild type. Progeny with both alleles are designated U and shaded blue and nt indicates a genotypic (rather than phenotypic) marker. D. Segregation data for furA. Parents were A34 (A) and NRRL1555 (N). Markers are: resistant (R) or sensitive (S) to 5-fluorouracil, the A or G nucleotide in the furA gene, madD (D) or wild type (WT) for phototropism, the sex phenotype is either (+) or (–) and equivalent PCR analysis for the sexM (M) or sexP (P) gene.