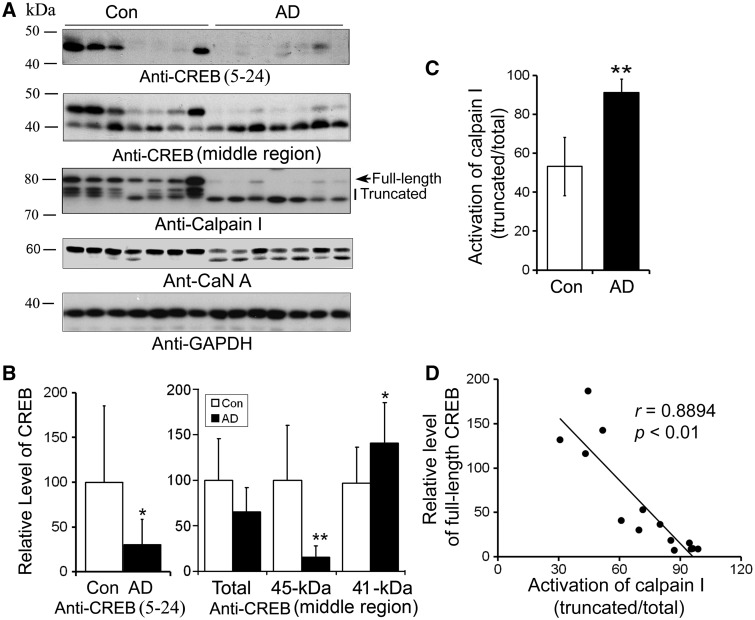
Figure 5.
The level of full-length CREB is decreased in AD brain and is correlated to activation of calpain I in human brain. (A) Western blots of CREB, calpain I and CaN A. Frontal cortical homogenates from seven AD and seven control cases were subjected to western blots developed with antibodies against CREB, calpain I, CaN A or GAPDH. (B) The level of full-length CREB was decreased and truncation of CREB was increased in AD brain significantly. Blots as shown in (A) developed with anti-CREB (upper panel) were quantitated by densitometry, and the levels of CREB was normalized with GAPDH and presented as mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (C) Truncation and activation of calpain I were significantly increased in AD brain. Arrow indicates full length of calpain I and vertical line indicates truncated and active form of calpain I. Blots as shown in (A) developed with anti-calpain I were quantitated by densitometry, the truncation and activation of calpain I were presented by the ratio of the truncated (76–78 kDa) over the total calpain I. (D) CREB level was correlated with the activation of calpain I in human brain. The relative activation of calpain I [truncated/(full length + truncated)] (x-axis) is plotted against the relative CREB level (y-axis).