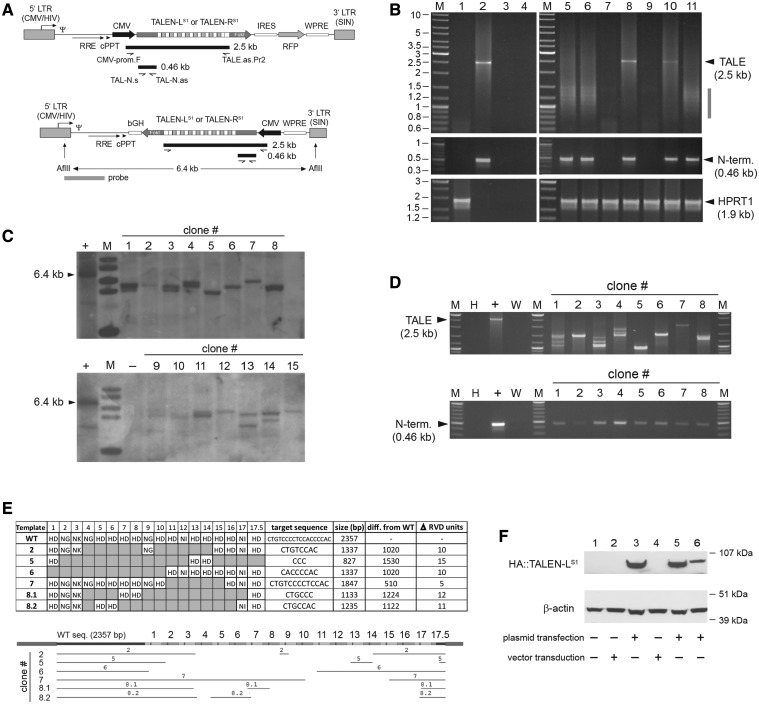
Figure 1.
Structural analyses of HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors harboring TALEN sequences in transduced cells. (A) Genetic organization of lentiviral vector constructs. Diagram of bicistronic pLV.TALEN-LS1.i.RFP and pLV.TALEN-RS1.i.RFP and of monocistronic pLV.TALEN-LS1 and pLV.TALEN-RS1 lentiviral vector transfer plasmids. The bicistronic constructs code for the AAVS1-specific custom-made nucleases TALEN-LS1 or TALEN-RS1 and, through an IRES sequence, an RFP reporter, whereas the monocistronic plasmids encode exclusively the AAVS1-specific designer nucleases. Each of the TALEN proteins are tagged by an HA antigen located close to their N-termini (not drawn). Gray boxes with broken arrow, hybrid 5′ LTR containing CMV and HIV-1 sequences; gray boxes without broken arrow, self-inactivating (SIN) 3′ LTR; Ψ, HIV-1 packaging signal; RRE, Rev-responsive element; cPPT, central polypurine tract; WPRE, Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element. In pLV.TALEN-LS1.i.RFP and pLV.TALEN-RS1.i.RFP, the ORFs are under the transcriptional control of the CMV promoter and the polyadenylation signal present within the SIN 3′ LTR, whereas the ORFs in pLV.TALEN-LS1 and pLV.TALEN-RS1 are under the control of the CMV promoter and the bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal (bGH). Primers, PCR products and Southern blot probe used are depicted as half-arrows, black bars and gray bar, respectively, and are drawn in relation to their respective vector DNA sequences. For the sake of simplicity, plasmid backbone sequences are not shown. The sizes of the PCR products expected from the amplification of full-length lentiviral vector genomes are indicated. The 6.4-kb AflII restriction fragment corresponding to intact DNA from LV.TALEN-LS1 or LV.TALEN-RS1 is also indicated. (B) PCR analyses of TALEN-encoding HIV-1-based lentiviral vector genomes following transduction of HeLa cells. PCR amplifications with the aid of the primers shown in Figure 1A were carried out using, as template, total cellular DNA from mock-transduced HeLa cells, plasmid pAd.ΔE1.TALEN-LS1.F50, plasmid pLV.CMV.eGFP or nuclease-free H20 (lanes 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively). PCR amplifications using the same primer pairs were performed in parallel on DNA extracted from HeLa cells transduced with integration-competent LV.TALEN-RS1 (lane 5), integrase-defective IDLV.TALEN-RS1 (lane 6), Ad.ΔE1.TALEN-RS1.F50 (lane 10) or integration-competent LV.TALEN-RS1.i.RFP (lane 11). Extra PCR controls supplementing those corresponding to lanes 1 through 4 were provided by using DNA isolated from HeLa cells exposed to an LV.TALEN-RS1 preparation made in parallel but deploying pUC19 instead of lentiviral vector packaging construct psPAX2 (lane 7) or incubated with pLV.TALEN-RS1 mixed or not mixed with the DNA transfection agent ExGen500 (lanes 8 and 9, respectively). Lanes M, Gene Ruler DNA Ladder Mix. A primer pair targeting the human HPRT1 served to control the integrity of the cellular DNA. (C) Clonal analysis. Southern blot analysis of AflII-digested genomic DNA from HeLa cell clones 1 through 15 stably transduced with LV.TALEN-LS1. The vector-specific probe that was used is shown in Figure 1A (horizontal gray bar). Lane M, 1 kb molecular-weight marker. The parental transfer plasmid pLV.TALEN-LS1 treated with AflII served as an internal control for intact vector DNA. (D) PCR screening of genomic DNA from HeLa cell clones stably transduced with LV.TALEN-LS1. Upper and lower panel, PCR products resulting from the use of the primer pairs CMV-prom.F/TALE.as.Pr2 and TAL-N.s/TAL-N.as, respectively, on HeLa cell clones 1 through 8 (note: clone 8 turned out to yield two closely sized and vector-specific amplicons, thus the nomenclature 8.1 and 8.2). PCR amplifications on plasmid pLV.TALEN-LS1 served as a positive control (+), whereas those on nuclease-free water (W) and HeLa genomic DNA (H) provided for negative controls. Lanes M, Gene Ruler DNA Ladder Mix. (E) Structural analyses of proviral vector DNA. DNA sequencing of amplicons retrieved from HeLa cell clones 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8 after PCR amplifications with primers CMV-prom.F and TALE.as.Pr2 (Figure 1D, upper panel). Upper panel, summary of the TALE repeat arrays present in the indicated LV.TALEN-LS1-transduced HeLa cell clones. The respective predicted target sites, lengths, size reduction in relation to the wild-type sequence and the number of 102-bp long TALE repeat units found to be deleted, are also indicated. Lower panel, alignment of the TALEN-LS1 DNA sequences retained in the various proviruses (horizontal thin lines) drawn in relation to the reference wild-type sequence (horizontal thick line). (F) TALEN protein detection. HA tag-directed western blot analysis of full-length TALEN-LS1 expression in 293T producer cells (lane 1), IDLV.TALEN-LS1- and LV.TALEN-LS1-transduced HeLa cells (lane 2 and lane 4, respectively) and in pLV.TALEN-LS1-transfected 293T cells used to generate these IDLV.TALEN-LS1 and LV.TALEN-LS1 vector preparations (lanes 3 and 5, respectively). Lane 6, HeLa cells transfected with pLV.TALEN-LS1. The β-actin served as loading control.