Figure 3.
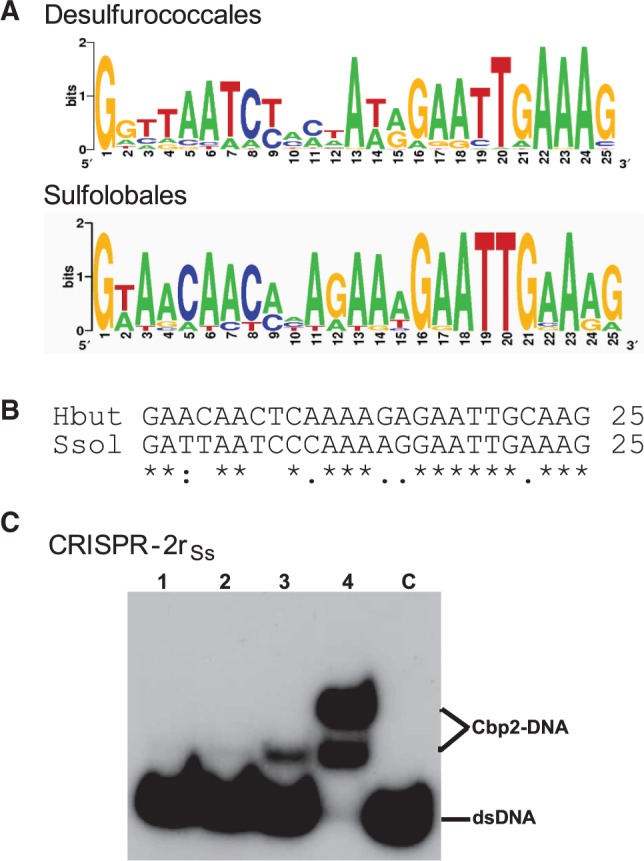
CRISPR repeat sequence conservation and Cbp2 binding dependence. (A) Logo-plot of the CRISPR repeats of Desulfurococcales—4 organisms, 13 repeats: H. butylicus (1), S. hellenicus (4), S. marinus (4) and P. fumarii (4) (CRISPR repeats are not available for T. cellulolyticus), and of Sulfolobales—16 organisms, 36 repeats (number of different repeats for each organism given in brackets): S. solfataricus P2 (3), S. solfataricus 98/2 (3), S. tokodaii (3), S. acidocaldarius (2), A. hospitalis (4), A. brierleyi (4), M. sedula (3) and S. islandicus strains REY15A (1), HVE 10/4 (2), L.S.2.15 (2), Y.N.15.51 (1), M.16.27 (1), Y.G.57.14 (1), M.14.25 (2), M.16.4 (2), L.D.8.5 (2). Logo plots were obtained using available software (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/). (B) CRISPR repeat alignment for H. butylicus and S. solfataricus P2. (C) Cbp2Hb binding to CRISPR-2rSs DNA. Cbp2Hb was incubated with 8 nM [32P] 5′-end labelled CRISPR-2rSs DNA at a 1, 2, 3 and 4 molar protein excess in lanes 1 to 4, respectively. Lane C—DNA substrate alone.
