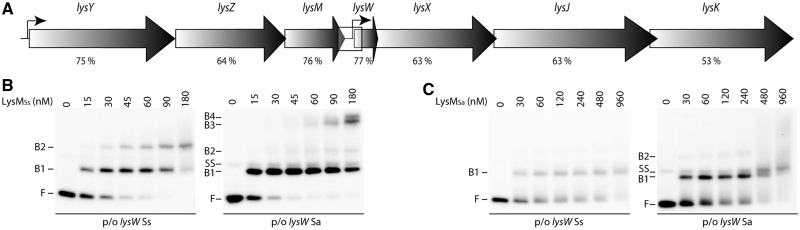
Figure 1.
Functional conservation of the LysM–lysW operator interaction in Sulfolobus. (A) Schematic overview of genomic organization of the lys locus. ORFs are depicted by arrows, with names of corresponding genes mentioned above. Transcription start sites are indicated with small black arrows. The genomic organization shown here is identical for all sequenced Sulfolobus species, and amino acid sequence identity between S. solfataricus and S. acidocaldarius orthologues is mentioned below each lys gene. The lysW promoter/operator region that is subject of the interaction analysis is indicated by a rectangle. (B) EMSAs of binding of LysMSs to the lysW control regions of S. solfataricus (on a 203-bp fragment) and S. acidocaldarius (on a 188 bp-fragment), as indicated. Protein concentrations are mentioned on top of the autoradiograph. Positions of free DNA (F), free single-stranded DNA (SS) and protein–DNA complexes (B1–B4) are pointed out. (C) EMSAs of binding of LysMSa to the lysW control regions of S. solfataricus and S. acidocaldarius, as indicated. Notations are the same as in subpanel (B).