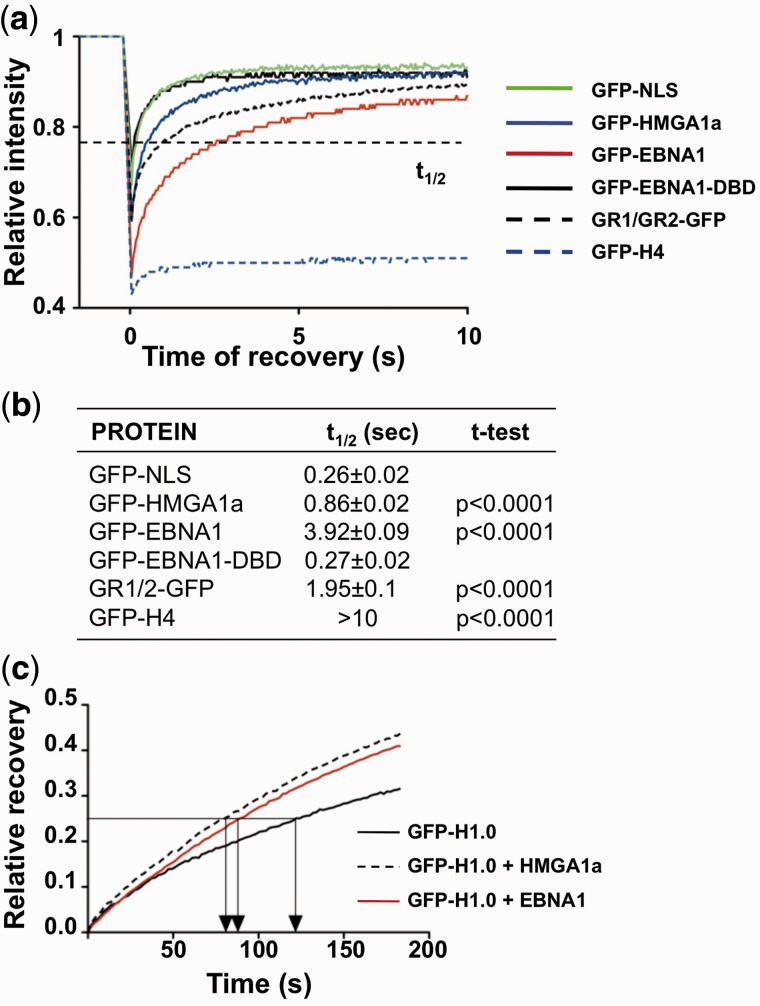
Figure 6.
EBNA1 is highly mobile on interphase chromatin and displaces histone H1. (a) The GR1 and GR2 domains mediate a highly dynamic interaction of EBNA1 with cellular chromatin. FRAP recovery curves of GFP-tagged proteins in transfected U2OS cells. The fast recovery of the FRAP signal for GFP-NLS indicates that the protein does not bind to chromatin, whereas the failure to recover the signal of GFP-H4 confirms the tight association with DNA. The FRAP recovery curve of EBNA1 and GR1/GR2 containing constructs was comparable with that of HMGA1a. (b) Compilation of the time required of 50% recovery of fluorescence (t1/2) in 20 cells. The curves were fitted with the Prism5 software and significance was calculated relative to GFP-NLS. (c) FRAP recovery curves of GFP-H1.0 in NIH2/4 cells co-transfected with GFP-H1.0 and either mCherry-LacR, mCherry-LacR-EBNA1 or mCherry-LacR-HMG1a. The faster recovery time of GFP-H1.0 in cells expressing mCherry-LacR-EBNA1 or mCherry-LacR-HMGA1a indicates that the proteins reduce the chromatin-binding of histone H1.