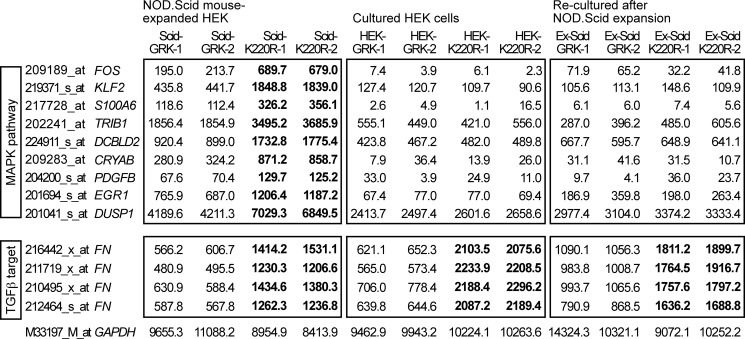
FIGURE 4.
Microarray gene expression profiling revealed up-regulation of MAPK pathway genes in NOD.Scid mouse-expanded HEK clones expressing GRK2-K220R. Microarray gene expression profiling was performed with HEK clones expanded in vivo in NOD.Scid mice (Scid, left panels), of the respective in vitro-cultured HEK cell clones (HEK, middle panels), and of re-cultured cells after NOD.Scid mouse expansion (Ex-Scid, right panels). Gene expression data from GRK2-expressing (GRK-1 and GRK-2) and GRK2-K220R-expressing HEK clones (K220R-1 and K220R-2) are shown. Microarray probe sets were selected according to the following criteria: (i) significant difference (p ≤ 0.01) between NOD.Scid mouse-expanded clones expressing GRK2-K220R (Scid-K220R-1; Scid-K220R-2) and GRK2 (Scid-GRK-1; Scid-GRK-2), (ii) >1.6-fold up-regulation in GRK2-K220R-expressing clones relative to GRK2-expressing clones, and (iii) involvement in the MAPK pathway according to gene ontology analysis. Probe sets with significant differences (K220R- relative to GRK2-expressing HEK cells/clones) are marked in bold. The following genes were identified: FOS, v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog; KLF2, Kruppel-like factor 2; S100A6, S100 calcium-binding protein A6, calcyclin; TRIB1, tribbles homolog 1; DCBLD2, discoidin, CUB and LCCL domain containing 2; CRYAB, crystallin, αB; PDGFB, platelet-derived growth factor β polypeptide; EGR1, early growth response 1; DUSP1, dual specificity phosphatase-1. Signal intensities of probe sets detecting the TGFβ target fibronectin (FN) were significantly lower in all GRK2-expressing HEK cells/clones indicative of TGFβ-antagonistic activity of GRK2. Selected data of two gene chips are presented for each group (two different clones/cell preparations per gene chip). The probe set detecting GAPDH is shown as a control.