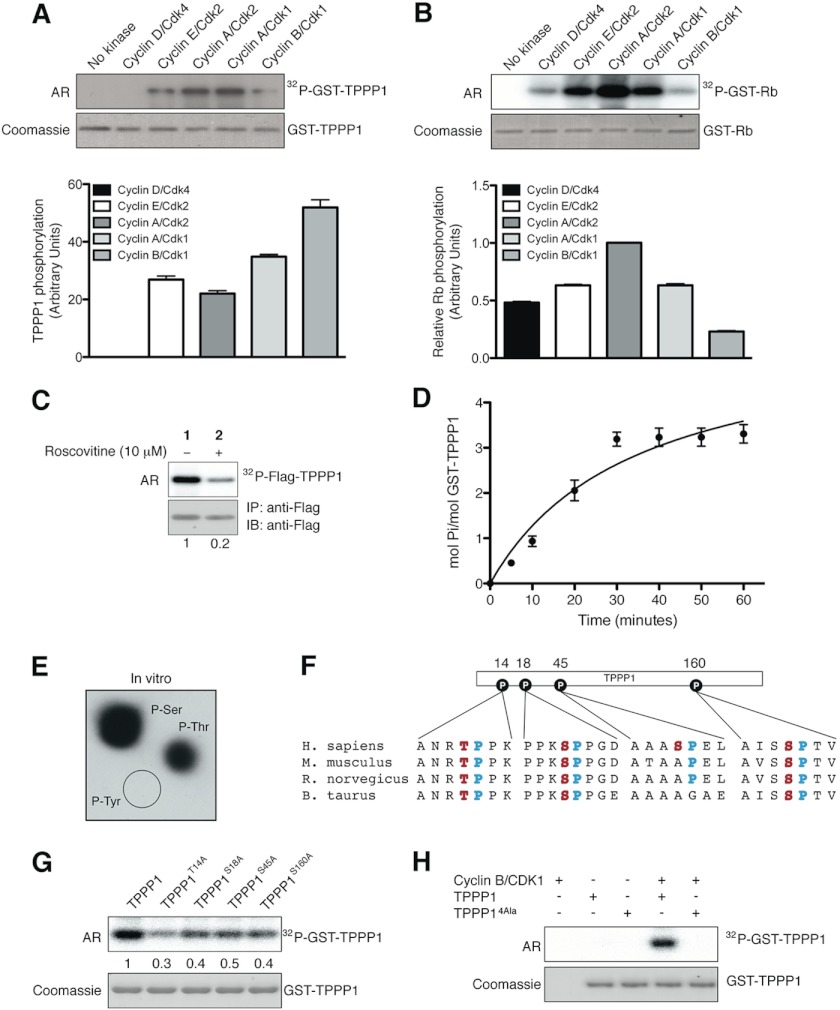
FIGURE 4.
TPPP1 is a Cyclin/Cdk substrate in vitro and in cells. A and B, TPPP1 is a Cdk substrate in vitro. In vitro kinase assays were performed in the presence of the bacterially expressed and purified TPPP1 (A) or Rb (B) proteins and the cyclin D/Cdk4, cyclin E/Cdk2, cyclin A/Cdk2, cyclin A/Cdk1, and cyclin B/Cdk1 complexes as described under “Experimental Procedures.” TPPP1 phosphorylation levels (A) were normalized according to cyclin/Cdk complex activities based on their level of Rb phosphorylation (B). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. C, TPPP1 is an in vivo Cdk substrate. U2OS cells transiently transfected with FLAG-TPPP1 were treated with roscovitine (10 μm) or vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) prior to incubation with [32P]orthophosphate (0.1 mCi/ml) for 6 h. TPPP1 phosphorylation in cells was determined by immunoprecipitation (IP) of the F-TPPP1 protein followed by autoradiography (AR) and immunoblotting (IB). D, TPPP1 is phosphorylated on 3–4 serine/threonine residues by Cdk1. Michaelis-Menten kinetics assays performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” revealed that Cdk phosphorylates TPPP1 on 3–4 residues. E, phosphoamino acid analysis of in vitro phosphorylated TPPP1 showed that TPPP1 is phosphorylated by Cdk on serine and threonine residues. F, amino acid sequence alignment of four mammalian TPPP1 species showing their evolutionary conservation, potential Cdk phosphorylation sites: TPPP1 Thr-14, Ser-18, Ser-45, and Ser-160 (red) and their minimal Cdk motif proline residue (+1; blue). G, alanine substitution mutations of TPPP1 Thr-14, Ser-18, Ser-45, or Ser-160 residues decreased their phosphorylation by cyclin B/Cdk1. In vitro kinase assays with cyclin B/Cdk1 and wild-type TPPP1, TPPP1-T14A, TPPP1-S18A, TPPP1-S45A, or TPPP1-S160A were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” H, the quadruple T14A/S18A/S45A/S160A (TPPP14Ala) mutations abolish TPPP1 phosphorylation by cyclin B/Cdk1 in in vitro kinase assays. The numbers below the panels in C and G represent their level of phosphorylation relative to the wild-type TPPP1 protein. Data in A, B, and D are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three and two independent experiments, respectively.