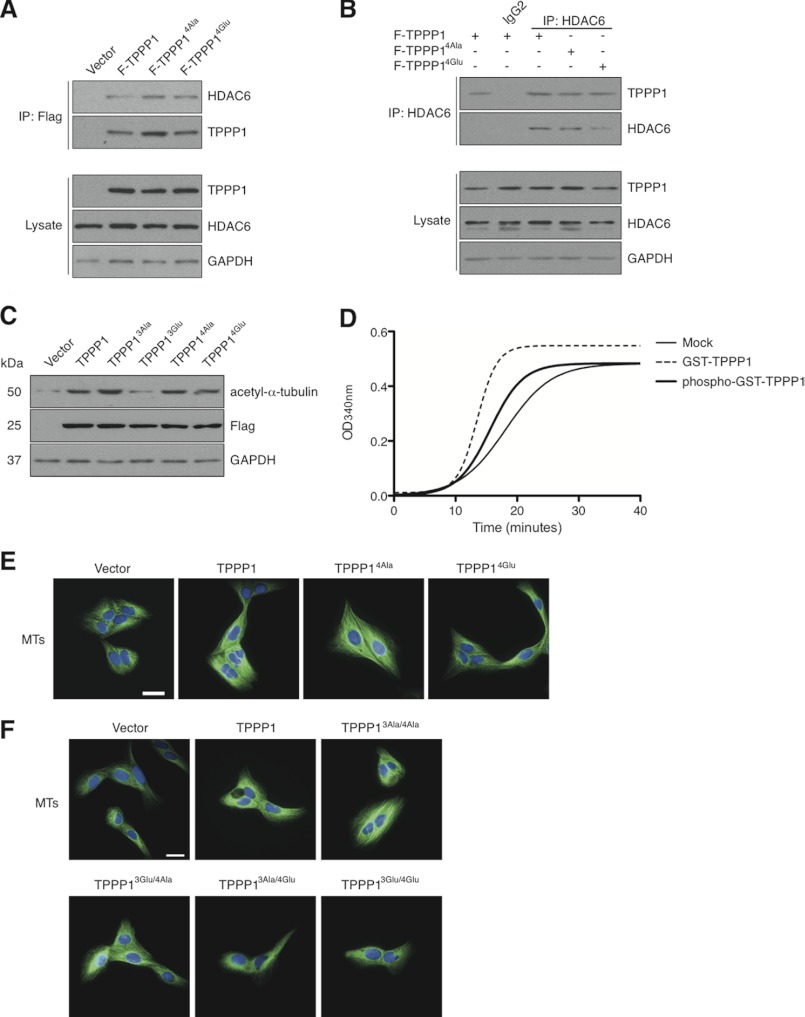
FIGURE 5.
Cdk-TPPP1 signaling inhibits its MT polymerizing activity. A, U2OS cells expressing F-TPPP1, F-TPPP14Ala, F-TPPP14Glu, or vector were immunoprecipitated (IP) and analyzed by immunoblotting together with cell lysates that were probed for FLAG-TPPP1, HDAC6, and GAPDH (loading control). B, U2OS cell extracts from A were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HDAC6 antibody and their interaction with F-TPPP1 proteins and total cell lysates were analyzed as described in A. C, stable U2OS cell line extracts expressing the indicated TPPP1 proteins or vector were immunoblotted for acetyl-α-tubulin, FLAG, and GAPDH (loading control) levels. D and E, TPPP1 phosphorylation by cyclin B/Cdk1 inhibits its MT polymerizing activity in vitro and in cells. D, in vitro MT polymerization assays in the presence of GST- or GST-TPPP1 phosphorylated in vitro by cyclin B/Cdk1 as described under “Experimental Procedures.” E, phosphorylation of TPPP1 by Cdk inhibits its microtubule polymerizing activity in cells. U2OS cells stably expressing wild-type TPPP1, TPPP14Ala, TPPP14Glu, or vector were stained for MTs (green) and nuclei (blue). Immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that expression of Cdk-mediated phosphomimetic TPPP1 (TPPP14Glu) reduces the level of MT staining compared with cells expressing wild-type and phosphoinhibitory TPPP1 (TPPP14Ala). F, only TPPP1 phosphorylation by Cdk inhibits its MT polymerizing activity. U2OS cells stably expressing wild-type TPPP1, TPPP13Ala/4Ala, TPPP13Glu//4Ala, TPPP13Ala/4Glu, TPPP13Glu/4Glu, or vector were analyzed as described in E. Scale bar is 50 μm.