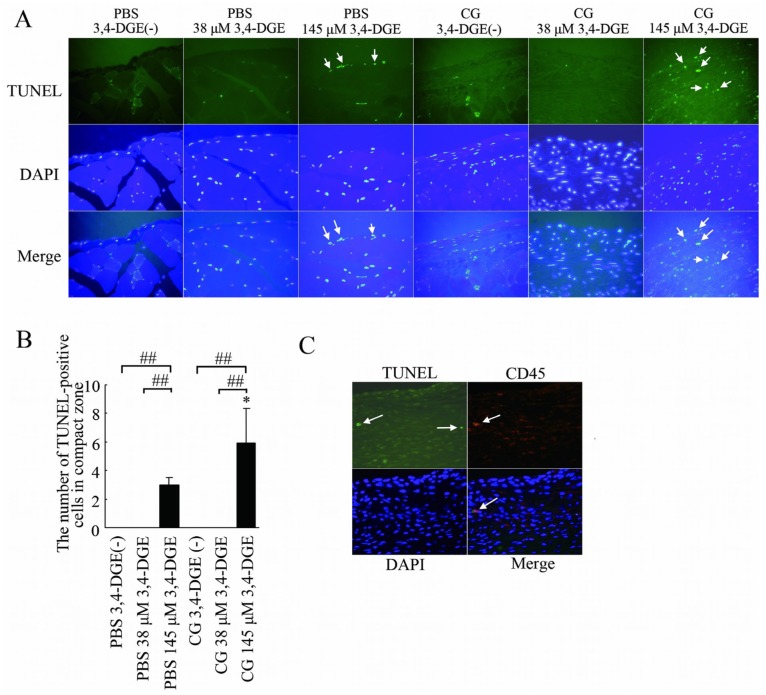
Figure 5.
— Apoptotic cells in the peritoneum. (A) TUNEL staining (green), DAPI staining (blue), and merged images. Mice treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) plus 145 μmol/L 3,4-dideoxyglucosone-3-ene (3,4-DGE) showed TUNEL-positive cells (arrows). Mice treated with chlorhexidine gluconate (CG) plus 145 μmol/L 3,4-DGE showed more TUNEL-positive cells than did mice treated with PBS+145 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (arrows). DAPI was used as nuclear staining. Most TUNEL-positive cells were also positive for DAPI. Number of mice: PBS without 3,4-DGE [PBS+3,4-DGE(-), n = 7]; PBS+38 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 5); PBS+145 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 5); CG+3,4-DGE(-) (n = 5); CG+38 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 6); CG+145 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 5). (B) Ratio of TUNEL-positive cells to DAPI-positive cells in the submesothelial area in mice. All values: mean ± standard error of the mean. * p < 0.05 versus mice treated with PBS and the same dose of 3,4-DGE; ## p < 0.01. (C) Triple staining for TUNEL (green), CD45 (red), and DAPI (blue) in mice (n = 5) treated with CG+145 μmol/L 3,4-DGE. Some of TUNEL-positive cells are leukocytes (arrows).